Introduction
Many people are talking about SaaS. SaaS applications are cool, but for us - the people who create and make them work, it represents a new challenge as we have to change the way we code and architect the solution.
A perfectly developed and architected SaaS application has to be:
- Multitenant
- Configurable
- Scalable
This article talks a little bit about being multitenant and configurable and provides a tool to help developers to achieve the configurable part.
For more information about SaaS applications and how to architect an SaaS application, read this.
Background
Multitenancy is not a universally accepted concept. However, as a developer you can think of multitenancy as a single application that can be used by many people with the same base needs but different specific needs. The users may or may not use the application at the same time, and so, the application must be able to cover those specific needs. For example, imagine an application used by the Help Desk departments in the same or in different companies. As you can imagine, each department/company will have to store different data, and each one will need a personalized UI.
An approach to solve the different data needs is the use of Metadata. For this sample, the DB uses the following tables:
Issue MetadataCatalog Metadata
Sorry for the MetadataCatalog and Metadata Table Names, more appropriate names would be MetadataCatalog->Metadata and Metadata->IssueExtensionData. The code works as it is but I leave this fix to you.
This DB design solves the personalized data problem. Now we have to solve the personalized UI problem and this sample code provides a tool that you can use to solve it.
Using the Code
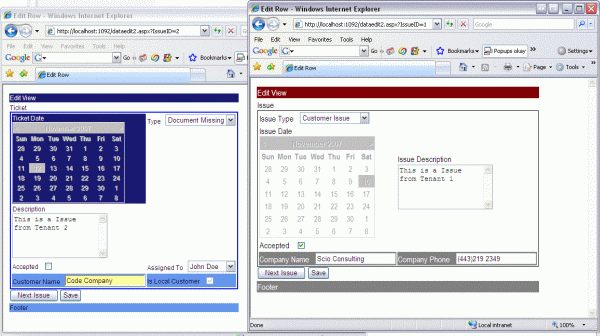
What does the sample code do? It takes a dataset and an HTML template as some of the parameters and renders a UI based on the HTML template and the data types of the dataset. So for example, if the template contains a tag to show a field called Field1, the code will generate the proper control for that data type, that means a TextBox for strings and numbers, CheckBox for boolean, Calendar for datetime, etc.
Note: This article focuses on the configurable problem of the SaaS applications, so please don't pay attention to the way in which I load the data.
To test the code, first of all you have to create the DB and the tables, the project provides 2 scripts(under the DB_Scripts folder), one is used to create Tables and the other is used to enter some sample data.
Create a Database named CITSS. Run the CreateTables.sql script, then run the CreateDemoData.sql script. Check for any errors.
Now you have to setup the DB connection. Go to the CITSS.UI.Base project and in the Code folder open the IssueHelper.vb file. Change the following line to meet your needs:
Private Const DBConn As String = _
"Server=127.0.0.1;Database=CITSS;uid=user;pwd=password;"
The core of the code is in the UIHelper class under the Code folder. There are two ways to generate the UI, as an HTML string or adding the controls to some ControlCollection. These are the functions that you will use:
Public Shared Function CreateUI(ByVal Data As DataSet,_
ByVal Template As String, ByVal LoadData As Boolean) As String
Public Shared Sub CreateUI(ByRef Controls As Web.UI.ControlCollection, _
ByVal Data As DataSet, ByVal Template As String, _
ByVal LoadData As Boolean)
Both Functions are commented in the code so take a look at them.
There are some Constants used in that file(UIHelper.vb) - these constants are related to the names of the Metadata and Extended table FIELDS, if you want to use other FIELD names, change them here as well:
Public Const CatalogColumnFieldID As String = "FieldID"
Public Const CatalogColumnFieldName As String = "FieldName"
Public Const CatalogColumnFieldType As String = "FieldType"
Public Const CatalogColumnLenght As String = "Length"
Public Const MetaDataColumnValue As String = "Value"
Public Const MetadataColumnFieldID As String = "FieldID"
To have a better understanding of what those fields mean, run the application and check the values in the database. NOTE: The Metadata catalog uses a field called FieldType, the value there must be a system type, example Int32, String, DateTime, Double, etc.
In this example, there are two available templates(under UITemplates folder) and two CSS available files(under CSSFiles folder). A template is an HTML file that contains the definition of our UI. To show some fields in the UI, use the following syntax:
For a normal field inside a normal table use:
<#TableName.TableField#>, example <#Issue.IssueDate#>
For an extended field use :
<#[CatalogTable.ExtendedTable].FieldName#>,
example <#[MetadataCatalog.Metadata].CompanyPhone|ReadOnly#>
Now, if your field is an ID and you want to use a combobox
to enter the value, use the following syntax:
For a normal table field:
<#TableName.TableField->FillFromTable.TableFieldID(FieldToShow)#>,
example <#Issue.IssueTypeID->IssueType.IssueTypeID(IssueTypeName)#>
For an extended field use:
<#[CatalogTable.ExtendedTable].FieldName->
FillFromTable.TableFieldID(FieldToShow)#>,
example <#[MetadataCatalog.Metadata].AssignedToID->
Users.UserID(UserName)#>
If you want to make the field read only, just add |ReadOnly to the field tag,
example, <#[MetadataCatalog.Metadata].CompanyPhone|ReadOnly#>
<#Issue.IssueDate|ReadOnly#>
The project has two web forms, DataEdit2.aspx and DataEdit.aspx, both of which work. The only difference between them is that, in DataEdit2.aspx we are adding the created controls to some Panel, and for DataEdit.aspx we receive the result of the CreateUI function as a string and then set it as the InnerHTML of some div.
Points of Interest
There is a lot that you can improve in the code, for example, right now the UI only generates TextBox, Calendar, Checkbox and ComboBox, you can implement more controls or add Custom Controls. Moreover, no validation is being performed and you have to implement some way to save the data.
History
