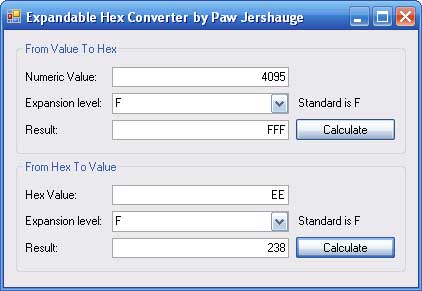

Introduction
This class uses the Hex algorithm idea and expands it. Or, more like the Base64 conversion.
The Class
public static class ExpandableHexConverter
{
public enum ExpandLevel
{
A = 11,
B,
C,
D,
E,
F,
G,
H,
I,
J,
K,
L,
M,
N,
O,
P,
Q,
R,
S,
T,
U,
V,
W,
X,
Y,
Z,
UseCaseSensitive = 62
}
public static string ToHex(long value, ExpandLevel ExpandBy)
{
return loopRemainder(value, (long)ExpandBy);
}
public static long ToInt64(string value, ExpandLevel ExpandBy)
{
value = validate(value, ExpandBy);
long returnvalue = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < value.Length; i++)
returnvalue += (long)Math.Pow((long)ExpandBy,
(value.Length - (i + 1))) * CharToVal(value[i]);
return returnvalue;
}
private static string loopRemainder(long value, long PowerOf)
{
long x = 0;
long y = Math.DivRem(value, PowerOf, out x);
if (y > 0)
return loopRemainder(y, PowerOf) + ValToChar(x).ToString();
else
return ValToChar(x).ToString();
}
private static char ValToChar(long value)
{
if (value > 9)
{
int ascii = (65 + ((int)value - 10));
if (ascii > 90)
ascii += 6;
return (char)ascii;
}
else
return value.ToString()[0];
}
private static long CharToVal(char value)
{
long chrval = (int)value;
if (chrval > 96)
return (chrval - 71) + 10;
else if (chrval > 64)
return (chrval - 65) + 10;
else
return int.Parse(value.ToString());
}
private static string validate(string input, ExpandLevel ExpandBy)
{
string validchars = "";
string rtnval = "";
for (long c = 0; c < (long)ExpandBy; c++)
validchars += ValToChar(c);
foreach (char i in input)
if (validchars.Contains(i.ToString()))
rtnval += i;
return rtnval;
}
}
Using the code
Normal hex looks like this:
string HexValue = ExpandableHexConverter.ToHex(255,
ExpandableHexConverter.ExpandLevel.F);
Result:
HexValue = FF
Expanded hex could look like this:
string HexValue = ExpandableHexConverter.ToHex(1295,
ExpandableHexConverter.ExpandLevel.Z);
Result:
Result:
HexValue = ZZ
Expanded hex could also look like this:
string HexValue = ExpandableHexConverter.ToHex(3843,
ExpandableHexConverter.ExpandLevel.UseCaseSensitive);
Result:
Result:
HexValue = zz
Some comparisons
The normal Hex Algorithm is Base 16, which is demonstrated here:
- F = 15 (0 to 15 = 16)
- FF = 255
- FFF = 4095
The expanded Hex Algorithm set to Z is Base 36, which is demonstrated here:
- Z = 35 (0 to 35 = 36)
- ZZ = 1295
- ZZZ = 46655 (11 times larger than normal Hex)
The expanded Hex Algorithm set to UseCaseSensitive is Base 62, which is demonstrated here:
- z = 61 (0 to 61 = 62)
- zz = 3843
- zz = 238327(58 times larger than normal Hex)
History
- 23. Nov. 2007 - The first version is posted.
- 23. Nov. 2007 - Article renamed...
