Introduction
This program will help you write the necessary code for doing base operations of your application's Data Layer (both Web and Windows applications). The function of this program is making a DAL class for easily selecting, manipulating and deleting records of the Database. The result is a simple class for each table in your database. The structure is described below in a schematic view.
Background
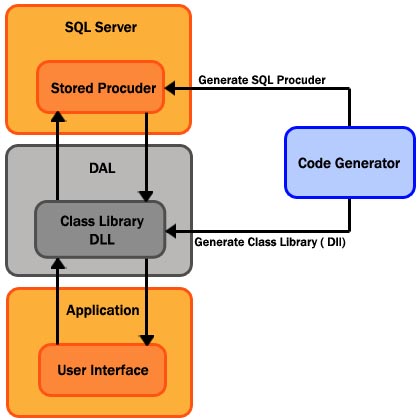
Using the Code
Class Structure
- Property
Insert method Update method Delete method Select method
Description
These generated properties indicate each field of a table. You may use them to get or set values in your application:
private string ConnectionString;
public City(string ConnStr)
{
ConnectionString = ConnStr;
}
private string m_Code;
public string Code
{
get { return m_Code; }
set { m_Code = value; }
}
private string m_Title;
public string Title
{
get { return m_Title; }
set { m_Title = value; }
}
private string m_Province_Code;
public string Province_Code
{
get { return m_Province_Code; }
set { m_Province_Code = value; }
}
This method uses generated stored procedures to Insert records into the database. It passes given values of each field to that stored procedure:
public void Insert(string Code , string Title , string Province_Code)
{
SqlConnection conn = new SqlConnection(ConnectionString);
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand("Insert_City", conn);
cmd.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure;
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue(@Code ,Code );
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue(@Title ,Title );
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue(@Province_Code ,Province_Code );
try
{
conn.Open();
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
catch
{}
finally
{
if (conn.State==ConnectionState.Open)
{
conn.Close();
}
conn.Dispose();
cmd.Dispose();
}
}
You can also use the second overload of the Insert method to insert a record using currently specified properties.
The Update method manipulates a record in database using the generated stored procedures. Such as above, this method calls the proper stored procedure with the given values:
public void Update(string Code , string Title , string Province_Code)
{
SqlConnection conn = new SqlConnection(ConnectionString);
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand("Update_City", conn);
cmd.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure;
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue(@Code ,Code );
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue(@Title ,Title );
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue(@Province_Code ,Province_Code );
try
{
conn.Open();
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
catch
{}
finally
{
if (conn.State==ConnectionState.Open)
{
conn.Close();
}
conn.Dispose();
cmd.Dispose();
}
}
This method uses generated stored procedures to delete a record from the database. It takes the value of the key field and calls the stored procedure using that value:
public void Delete(string ID)
{
SqlConnection conn = new SqlConnection(ConnectionString);
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand("Delete_City", conn);
cmd.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure;
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue(@ID,ID);
try
{
conn.Open();
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
catch
{}
finally
{
if (conn.State==ConnectionState.Open)
{
conn.Close();
}
conn.Dispose();
cmd.Dispose();
}
}
Use this method to select a record set from a table to use later in your application. This method returns a dataset object using the generated stored procedure:
private DataSet Select()
{
SqlConnection conn = new SqlConnection(ConnectionString);
SqlDataAdapter cmd = new SqlDataAdapter("Select_City", conn);
DataSet dts = new DataSet();
try
{
conn.Open();
cmd.Fill(dts);
return dts;
}
catch
{
return null;
}
finally
{
if (conn.State==ConnectionState.Open)
{
conn.Close();
}
conn.Dispose();
cmd.Dispose();
}
}
SQL Transact
This program can generate transact-SQL to reach the nice methodology of "Fat Server and Thin Client". Below is the generated code we talk about:
Insert
CREATE PROCEDURE [insert_City]
(
@Code [int],
@Title [nvarchar](50),
@Province_Code [int]
)
AS INSERT INTO City
(
Code,
Title,
Province_Code
)
VALUES
(
@Code,
@Title,
@Province_Code
)
Update
CREATE PROCEDURE [update_City]
(
@Code [int],
@Title [nvarchar](50),
@Province_Code [int]
)
AS UPDATE City
SET
Code = @Code,
Title = @Title,
Province_Code = @Province_Code
WHERE
(
ID=@ID
)
Delete
CREATE PROCEDURE [delete_City]
(@ID [int])
AS
DELETE [City]
WHERE
([ID] = @ID)
Select
CREATE PROCEDURE [Select_City]
AS
SELECT [ID],
[Code],
[Title],
(Select Title FROM Province WHERE Code=Province_Code) as Province
FROM
City
Application Manual

After you run the program, you must choose the destination database in the login form to generate required stored procedures.
After login, you see the main form such as the above picture.

Left Zone
- Database structure contains all tables and their fields. You can right click on each table and choose the desired item to view DAL class or related stored procedures from the context menu.
Content Zone
- You see the generated class in this window. To use it later, you should save the content in a *.cs file using toolbar.
- You see the generated transact-SQL codes for creating stored procedures in this window. You may parse or execute them immediately or save them for later use.
Right Zone
- You can see the properties of a field you select in the left zone.
