Introduction
Out of the box, Microsoft SharePoint has a very rich set of features, but sometimes you need more, or something a little different, to meet the needs of your project. This article will discuss various methods of presenting the UI for SharePoint list forms, such as the New, Edit, and Display forms used when adding an item to a list, or viewing and editing items.
Background
There is a great deal of content on the web describing how to customize SharePoint list forms using InfoPath or SharePoint Designer. While those methods can meet some requirements, they certainly can't cover everything. InfoPath is quick and easy and is used throughout SharePoint, particularly for Workflow forms, however, you can't use JavaScript or code-behind for processing, nor can you use CSS to style the form. Although SharePoint Designer does allow you to apply CSS and use JavaScript because the forms are Site Pages, you are restricted from using code-behind or embedded code. Additionally, SharePoint Designer may not be available to everyone, nor does it produce a reusable solution.
Examples in this article were created with Visual Studio 2010 for SharePoint Server 2010 Foundation and above. This article is not about creating ContentTypes or an in-depth discussion of SharePoint lsts. It is assumed the reader has experience with SharePoint administration, such as creating custom lists, and ASP.NET development.
Lists and ContentTypes
Within SharePoint, data is stored in lists that have one or more ContentTypes associated with them. This allows for a great deal of flexibility for organizing and storing data. For the purposes of this article, I'll create a ContentType to demonstrate the functionality I'll be discussing.
<Elements xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/sharepoint/">
<ContentType ID="0x0100b10e34ab90214c4fa9efbb7653c208d8"
Name="CP Project Base"
Group="Code Project"
Description="Demo contenttype for CodeProject article"
Inherits="TRUE"
Version="0">
<FieldRefs>
<FieldRef ID="{a9f5f963-cd43-437f-9832-fa340e50334a}"
Name="ProjectName" DisplayName="Name"/>
<FieldRef ID="{c55b0ed1-c874-491e-914d-621abd9066f6}"
Name="ProjectDescription" DisplayName="Description"/>
<FieldRef ID="{64CD368D-2F95-4BFC-A1F9-8D4324ECB007}"
Name="StartDate" DisplayName="Start"/>
<FieldRef ID="{8A121252-85A9-443D-8217-A1B57020FADF}"
Name="_EndDate" DisplayName="End"/>
</FieldRefs>
</ContentType>
</Elements>
As you can see, nothing groundbreaking here. The ContentType uses two custom site columns and two built-in site columns, and is the base I'll be using to demonstrate the features and functionality surrounding SharePoint list forms.
SharePoint List Forms
After creating a custom list and associating the CP Project Base ContentType with it, when clicking on the Add new item link, you should see a dialog similar to this:
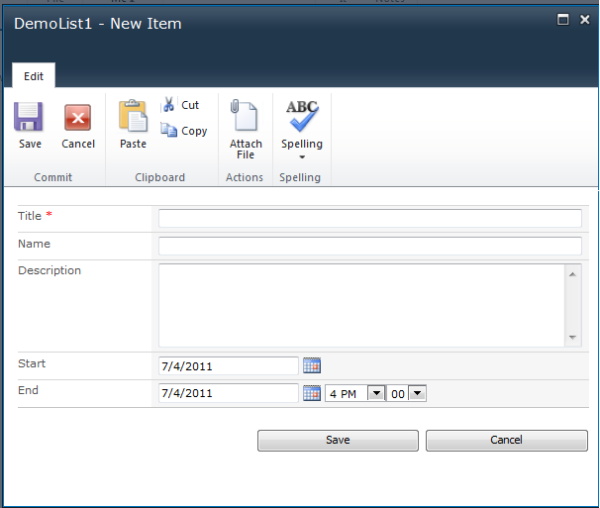
This is the default form that SharePoint displays for all lists, with the exception of Document Libraries, which I won't be covering in this article. How does this form get displayed and how does SharePoint know what to display?
List Definition Schema
All SharePoint lists have a schema file that defines the content and behavior of any list that is created from it.
="1.0"="utf-8"
<List xmlns:ows="Microsoft SharePoint"
Title="CPProject Base List Def"
FolderCreation="FALSE"
Direction="$Resources:Direction;"
Url="Lists/SharePointListForms-CPProjectListDef"
BaseType="0"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/sharepoint/">
<MetaData>
<ContentTypes>
<ContentType ID="0x0100b10e34ab90214c4fa9efbb7653c208d8"
Name="CP Project"
Group="Code Project"
Description="Demo contenttype for CodeProject article"
Inherits="TRUE"
Version="0">
<FieldRefs>
<FieldRef ID="{a9f5f963-cd43-437f-9832-fa340e50334a}"
Name="ProjectName" DisplayName="Name" />
<FieldRef ID="{c55b0ed1-c874-491e-914d-621abd9066f6}"
Name="ProjectDescription" DisplayName="Description" />
<FieldRef ID="{64CD368D-2F95-4BFC-A1F9-8D4324ECB007}"
Name="StartDate" DisplayName="Start" />
<FieldRef ID="{8A121252-85A9-443D-8217-A1B57020FADF}"
Name="_EndDate" DisplayName="End" />
</FieldRefs>
</ContentType>
</ContentTypes>
<Fields>
<Field ID="{a9f5f963-cd43-437f-9832-fa340e50334a}" Name="ProjectName"
DisplayName="Name" Group="Code Project" Type="Text" />
<Field ID="{c55b0ed1-c874-491e-914d-621abd9066f6}" Name="ProjectDescription"
DisplayName="Description" Group="Code Project" Type="Note" />
<Field ID="{8A121252-85A9-443d-8217-A1B57020FADF}" Name="_EndDate"
Group="$Resources:core,Base_Columns;" Type="DateTime"
DisplayName="$Resources:core,End_Date;"
Format="DateTime"
SourceID="http://schemas.microsoft.com/sharepoint/v3/fields"
StaticName="_EndDate">
<Default>[today]</Default>
</Field>
<Field ID="{64cd368d-2f95-4bfc-a1f9-8d4324ecb007}" Name="StartDate"
SourceID="http://schemas.microsoft.com/sharepoint/v3"
StaticName="StartDate"
Group="$Resources:core,Base_Columns;"
Type="DateTime" Format="DateOnly"
DisplayName="$Resources:core,Start_Date;">
<Default>[today]</Default>
</Field>
</Fields>
<Views>Removed for brevity</Views>
<Forms>
<Form Type="DisplayForm" Url="DispForm.aspx"
SetupPath="pages\form.aspx" WebPartZoneID="Main" />
<Form Type="EditForm" Url="EditForm.aspx"
SetupPath="pages\form.aspx" WebPartZoneID="Main" />
<Form Type="NewForm" Url="NewForm.aspx"
SetupPath="pages\form.aspx" WebPartZoneID="Main" />
</Forms>
</MetaData>
</List>
As you can see from this example, the ContentType type and fields that it contains are defined along with any views that are available for a list instance created from this template. The Views elements have been removed for brevity here but the full version is available in the code download associated with this article. This should all be familiar to you and I won't go into the details of these elements here.
The element we are concerned about for this discussion is the Forms element.
<Forms>
<Form Type="DisplayForm" Url="DispForm.aspx"
SetupPath="pages\form.aspx" WebPartZoneID="Main" />
<Form Type="EditForm" Url="EditForm.aspx"
SetupPath="pages\form.aspx" WebPartZoneID="Main" />
<Form Type="NewForm" Url="NewForm.aspx"
SetupPath="pages\form.aspx" WebPartZoneID="Main" />
</Forms>
This is where the default forms used for displaying, editing, and creating new list items are defined.
Type attribute describes the type of the form, New, Edit or Display.Url attribute is the path to the form that will be provisioned, and is relative to the list instance that is created. For instance: http://mysite/Lists/DemoList/NewForm.aspx.SetupPath attribute is the path to the form that will be used to provision the Url form. This site page is located at <SharePoint Root>\14\TEMPLATE\Pages.WebPartZoneID attribute relates to the WebPartZones defined in the RenderingTemplates, which I'll discuss shortly.
Using the ContentType to control form display
One of the simplest ways to manipulate what is displayed on the list forms is to use the ContentType definition.
Take the scenario where, using the demo ContentType, it is not necessary, or desirable, for a user to fill in the EndDate field when creating a new item. Perhaps this is calculated elsewhere using other business logic, or in response to list events or workflows. As you saw previously, this field is displayed by default, but this can be changed using the ShowInXXXForm attributes.
To prevent the field from showing up in the new item form, I'll add the ShowInNewForm attribute and give it a value of FALSE. There are similarly named attributes that relate to the edit and display forms, ShowInEditForm and ShowInDisplayForm, respectively.
<FieldRef ID="{8A121252-85A9-443D-8217-A1B57020FADF}"
Name="_EndDate" DisplayName="End" ShowInNewForm="FALSE"/>
Once again, after creating a list instance from the list definition for the modified ContentType, you will see the EndDate is not displayed when adding a new item. However, it is available on the item display and edit pages.


Default Form Construction
As described above, the forms used for a list instance are provisioned from the page defined in the SetupPath attribute, Pages\fom.aspx. Within this page, like all SharePoint pages, there are a number of content server controls defined. For this discussion, we are concerned with PlaceHolderMain as follows:
<asp:Content ContentPlaceHolderId="PlaceHolderMain" runat="server">
<SharePoint:UIVersionedContent UIVersion="4" runat="server">
<ContentTemplate>
<div style="padding-left:5px">
</ContentTemplate>
</SharePoint:UIVersionedContent>
<table cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0"
id="onetIDListForm" style="width:100%">
<tr>
<td>
<WebPartPages:WebPartZone runat="server"
FrameType="None" ID="Main" Title="loc:Main" />
<img src="http://www.codeproject.com/_layouts/images/blank.gif"
width='590' height='1' alt="" />
</td>
</tr>
</table>
<SharePoint:UIVersionedContent UIVersion="4" runat="server">
<Elements xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/sharepoint/">
<ContentType
ID="0x0100a5d5cfc1e7ca4947bfa173184c15334c"
Name="StateLookup"
Group="LookupTest"
Description="My Content Type"
Inherits="TRUE"
Version="0"><FieldRefs><FieldRef
ID="{fa564e0f-0c70-4ab9-b863-0177e6ddd247}"
Name="Title" Required="TRUE" Hidden="TRUE"
ShowInNewForm="TRUE" ShowInEditForm="TRUE"
ReadOnly="FALSE" PITarget="" PrimaryPITarget=""
PIAttribute="" PrimaryPIAttribute=""
Aggregation="" Node="" /></FieldRefs></ContentType></Elements>
<ContentTemplate>
</div>
</ContentTemplate>
</SharePoint:UIVersionedContent>
</asp:Content>
We can narrow the discussion even further to only be concerned with the WebPartZone with ID="Main". This corresponds to the WebPartZoneId attribute I alluded to earlier, and is where the list item fields will be rendered. SharePoint inserts a ListFormWebPart into this WebPartZone that will render the contents of the list item from a RenderingTemplate matching the optional Template attribute. If not defined, this will default to ListForm. The use of the default ListFormWebPart can be overridden by setting the UseDefaultListFormWebPart attribute to false and supplying WebParts in the AllUsersWebPart elements in the list definition schema.
<Form Type="NewForm" Url="NewForm.aspx" SetupPath="pages\form.aspx"
WebPartZoneID="Main" UseDefaultListFormWebPart="False">
<WebParts>
<AllUsersWebPart WebPartZoneID="Main" WebPartOrder="1">
<
Admittedly, this is not a very useful implementation, but it does at least show how to include additional WebParts in the List form. To get more control over the display, you need to create a custom RenderingTemplate.
RenderingTemplates
Because SharePoint is built to support a large number of customizations, it would be impossible to create a form or WebPart to handle each situation. To overcome this, the ListFormWebPart is a template control, meaning that it accepts an ITemplate derived control that is used to render the UI as necessary based on what type of list is being displayed and what mode it is in, display, edit, or new.
protected override void CreateChildControls()
{
if (!this.hideWebPart)
{
if (base.PageComponent != null)
{
this.ItemContext.CurrentPageComponent = base.PageComponent;
}
if (((SPContext.Current != null) && SPContext.Current.IsDesignTime) ||
(this.UseLegacyForm() || (this.Template == null)))
{
base.CreateChildControls();
}
else
{
this.Controls.Clear();
TemplateContainer container = new TemplateContainer {
ControlMode = PageTypeToControlMode(this.pageType),
ItemContext = this.ItemContext
};
this.Template.InstantiateIn(container);
this.Controls.Add(container);
}
}
}
[WebPartStorage(Storage.None), DefaultValue((string) null),
Browsable(false), TemplateContainer(typeof(TemplateContainer))]
public ITemplate Template
{
get
{
if ((this.template == null) && (this.TemplateName != null))
{
this.template = SPControlTemplateManager.GetTemplateByName(this.TemplateName);
}
return this.template;
}
set
{
this.template = value;
}
}
The templates used for the UI in the ListViewWewPart are contained in RenderingTemplates that can be found in <SharePoint Root>\14\TEMPLATE\CONTROLTEMPLATES\DefautlTemplates.ascx. This UserControl contains 145 RenderingTemplates that are used to display fields, such as NumberField and CurrencyField, and UI for forms, such as SurveyForm or WkiEditForm. For this discussion, we are interested in the RenderingTemplate with ID ListForm.
<SharePoint:RenderingTemplate id="ListForm" runat="server">
<Template>
<span id='part1'>
<SharePoint:InformationBar ID="InformationBar1" runat="server"/>
<div id="listFormToolBarTop">
<wssuc:ToolBar CssClass="ms-formtoolbar" id="toolBarTbltop"
RightButtonSeparator=" " runat="server">
<Template_RightButtons>
<SharePoint:NextPageButton runat="server"/>
<SharePoint:SaveButton runat="server"/>
<SharePoint:GoBackButton runat="server"/>
</Template_RightButtons>
</wssuc:ToolBar>
</div>
<SharePoint:FormToolBar ID="FormToolBar1" runat="server"/>
<SharePoint:ItemValidationFailedMessage
ID="ItemValidationFailedMessage1" runat="server"/>
<table class="ms-formtable" style="margin-top: 8px;" border="0"
cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" width="100%">
<SharePoint:ChangeContentType ID="ChangeContentType1" runat="server"/>
<SharePoint:FolderFormFields ID="FolderFormFields1" runat="server"/>
<SharePoint:ListFieldIterator ID="ListFieldIterator1" runat="server"/>
<SharePoint:ApprovalStatus ID="ApprovalStatus1" runat="server"/>
<SharePoint:FormComponent ID="FormComponent1"
TemplateName="AttachmentRows" runat="server"/>
</table>
<table cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0"
width="100%"><tr><td class="ms-formline">
<img src="/_layouts/images/blank.gif" width='1' height='1'
alt="" /></td></tr></table>
<table cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" width="100%"
style="padding-top: 7px"><tr><td width="100%">
<SharePoint:ItemHiddenVersion ID="ItemHiddenVersion1" runat="server"/>
<SharePoint:ParentInformationField
ID="ParentInformationField1" runat="server"/>
<SharePoint:InitContentType ID="InitContentType1" runat="server"/>
<wssuc:ToolBar CssClass="ms-formtoolbar" id="toolBarTbl"
RightButtonSeparator=" " runat="server">
<Template_Buttons>
<SharePoint:CreatedModifiedInfo runat="server"/>
</Template_Buttons>
<Template_RightButtons>
<SharePoint:SaveButton runat="server"/>
<SharePoint:GoBackButton runat="server"/>
</Template_RightButtons>
</wssuc:ToolBar>
</td></tr></table>
</span>
<SharePoint:AttachmentUpload ID="AttachmentUpload1" runat="server"/>
</Template>
</SharePoint:RenderingTemplate>
As you can see, in this template, there are a number of different controls, such as FormToolBar and InformationBar, that SharePoint uses to display the UI components we have seen it the List forms. The one of particular interest is ListFieldIterator. This is the control that actually displays the fields, with labels and edit or display controls, many of which also use RenderTemplates.
To create and use a custom RenderingTemplate, I'll start by copying the ListForm template from DefaultTeamplates.ascx and placing it in the newly created UserControl in my project. One point to note here is when adding a UserControl via Visual Studio 2010, it will create a folder under the mapped CONTROLTEMPLATES folder for the new file. However, this won't work for RenderingTemplates. The SPControlTemplateManager.GetTemplateByName method only looks in the CONTROLTEMPLATES folder, not in sub-folders, so you'll need to make sure to move this file out of the sub-folder.
To use this template, you must modify the ContentType element in the Contenttype Element.xml file as follows.
<XmlDocuments>
<XmlDocument NamespaceURI="http://schemas.microsoft.com/sharepoint/v3/contenttype/forms">
<FormTemplates xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/sharepoint/v3/contenttype/forms">
<New>CPListForm</New>
</FormTemplates>
</XmlDocument>
</XmlDocuments>
The value specified in the New element must match the ID attribute in the RenderingTemplate.
There are two very big and not well documented issues that may present themselves when using a custom RenderingTemplate. First, you may notice the default RenderingTemplate is used rather than the custom one you have created. This is because of the Inherits attribute on the ContentType. For an as yet to be explained reason, it must be either removed or set to false so the custom RenderingTemplate will be used.
Inherits="FALSE"
The second issue come when using the default RenderingTemplate from DefaultTemplates.ascx as base. As can be seen above it includes two instances of the wssuc:ToolBar control.
<wssuc:ToolBar CssClass="ms-formtoolbar" id="toolBarTbltop"
RightButtonSeparator=" " runat="server">
<Template_RightButtons>
<SharePoint:NextPageButton runat="server"/>
<SharePoint:SaveButton runat="server"/>
<SharePoint:GoBackButton runat="server"/>
</Template_RightButtons>
</wssuc:ToolBar>
When you create a list and try to display the new item form, you may be surprised to see nothing rendered, as in the image below. No error messages, no exception, just an empty form.

The problem is when a new User Control is created via Visual Studio, it does not include the Register tag for the Toolbar.
<%@ Register TagPrefix="wssuc" TagName="ToolBar" src="~/_controltemplates/ToolBar.ascx" %>
After adding this tag, the form will be rendered using the custom RenderingTemplate as expected.

Custom List Forms
One more way to customize the List forms is to use a custom Application Page. This gives you full control over the UI, and you must implement all functionality, including any toolbars, buttons, or fields that are required.
Using a custom list form is similar to the RenderingTemplate method described above, except you use the FormUrls element rather than the FormTemplates element. The value of the New element is the path to the Application Page that will be used. In this example, I am placing the page just as any other Application Page used within the site, under the LAYOUTS folder and within a subfolder for the feature.
<XmlDocuments>
<XmlDocument
NamespaceURI="http://schemas.microsoft.com/sharepoint/v3/contenttype/forms/url">
<FormUrls xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/sharepoint/v3/contenttype/forms/url">
<New >_layouts/SharePointListForms/CPNewItem.aspx</New>
</FormUrls>
</XmlDocument>
</XmlDocuments>
As with the previous example, the Application Page will only be used if the ContentType is using Inherits=FALSE.

As you can see, the form is a blank slate, no toolbars or other elements, it is up to the developer to construct the page and provide the functionality as necessary.
Conclusion
In this article, I have reviewed various methods for displaying UI for SharePoint List forms, from simply hiding a field to full customization using an Application Page. As with most of SharePoint, there are many ways to accomplish the same thing, choosing which method is best for a situation is based on knowledge and experience. I hope this article has contributed to both.
Points of Interest
One main point to keep in mind when using RenderingTemplate or Application Page is the ContentType must use Inherits=false.
History
- 7/9/2011: Initial posting.
- 7/11/2011: Updated source code.
