Introduction
The idea about the FixIndexArray class came to me when I was looking for an array structure which will allow:
- To have direct access to an item by index, like a
List<T>. - To guarantee the same index during deleting an item, like a
Dictionary<int,T> (analogue of a DB primary key). - To have higher performance of deleting/adding an item than a
Dictionary<int,T>.
As a result, Ideveloped the class FixIndexArray. The final performance result shown on the picture below proves that it meets all the above requirements.
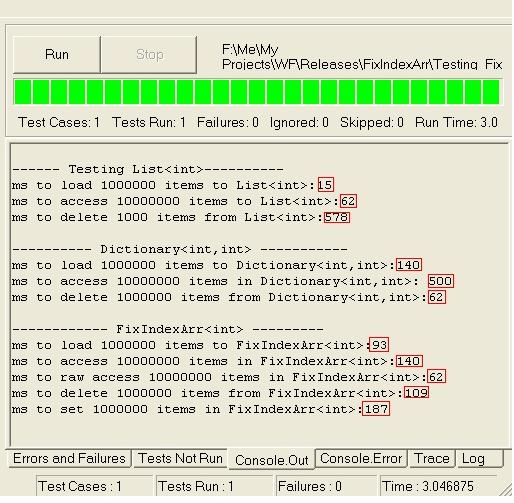
Using the code
Using the class cFixIndexArr is very straightforward, and API is very similar to List<T>.
private void PrintArr(cFixIndexArr<int> arr) {
Console.Write("Array : ");
foreach(int val in arr) {
Console.Write(string.Format("{0}, ", val));
}
}
[Test]
public void UseCase() {
Console.WriteLine(
"Create the FixIndexArr of integers with default capacity 10"
);
cFixIndexArr<int> arr = new cFixIndexArr<int>(10);
Console.WriteLine("Load array: {0,10,20,...90}");
for(int i=0; i<10; i++) {
arr.Add(i*10);
}
this.PrintArr(arr);
Console.WriteLine("\r\n\r\nDelete elements 1, 3, 5, 7, 9");
arr.Remove(1);
arr.Remove(3);
arr.Remove(5);
arr.Remove(7);
arr.Remove(9);
this.PrintArr(arr);
Console.WriteLine(
"\r\n\r\nAdd element '11', '22', '33', '44', '55', '66','77'"
);
arr.Add(11);
arr.Add(22);
int index33 = arr.Add(33);
arr.Add(44);
arr.Add(55);
arr.Add(66);
arr.Add(77);
this.PrintArr(arr);
Console.WriteLine("\r\n\r\nReplacing element 33 by 3333");
arr[index33] = 3333;
this.PrintArr(arr);
Console.WriteLine(
"\r\n\r\nDelete element 3333 and use it for element 4444"
);
arr.Remove(index33);
arr[index33] = 4444;
this.PrintArr(arr);
}
This code produces the following result:

How does it work?
The idea behind is simple: The class FixIndexArr<T> uses an array valArr of type List<T> for elements itself, and a helper array deletedIndexArr of type List<cItem> for tracking the deleted indexes. The structure cItem is a helper, and contains information about deleted indices in a double linked list manner:

