Introduction
The main purpose of this article is to understand how to monitor a group of Linked SQL Servers from a SQL Server.
Before I begin, I need to make things clear:
- This article makes use of Linked Server Technique and Socket Programming, which I will not discuss since there are other articles available on these subjects. But any questions, bugs and suggestions are most welcome.
Although prior knowledge of this subject will certainly help you, it is not mandatory. - This article is about a framework on how to perform monitoring, therefore it is quite possible that you may have a different idea of doing it.
Usefulness
This project can be used for any basic database monitoring. But it was designed purposefully for production support monitoring, where in database tables are monitored for certain data.
An example which I can provide is for Banking domain, where certain transactions should be moved to down system at predetermined schedule. Once these transactions are moved, their status is updated in the database as sent to down system.
Here we could set up this monitoring to check if the transaction has been sent? Otherwise raise the alert to the production support guys!
Monitoring Architect
For any Basic Monitoring System, the below mentioned objects are needed:
- Monitoring System - Object which monitors the system and raises the alert
- Alert Scheduling - For periodic scheduling of Monitoring System (Point 1)
- Alert Dispatcher - Dispatches the alerts
- Alert Receiver - System which receives the alert
Let us see how the above objects are provided to us by SQL Server and which ones we need to develop:
- SQL Job - For Alert Scheduling (Point 2)
- Linked Server Functionality - For Monitoring System (Point 1)
The remaining components Dispatch Alert and Receive Alert need to be developed:
AlertDispatcher - It is simple console based socket client which sends the Alert message to the listening socket Server. AlertReceive - It is an MFC dialog based socket application which displays the Alert sent by AlertDispatcher.
Setting up the Monitoring System
Before we can start monitoring any server, we need to Register Remote SQL server as linked servers:
To add Linked Server, the code given below can be used based on authentication scheme:
A. Windows Authentication:-
EXEC sp_addlinkedserver
@server = 'LinkName',
@srvproduct = 'SQLServer OLEDB Provider',
@provider = 'SQLOLEDB',
@datasrc = 'ServerIP_OR_NAME'
EXEC sp_addlinkedsrvlogin 'LinkName', 'true', null, null, null
B. Sql Authentication:-
EXEC sp_addlinkedserver
@server = 'LinkName',
@srvproduct = 'SQLServer OLEDB Provider',
@provider = 'SQLOLEDB',
@datasrc = 'ServerIP_OR_NAME'
EXEC sp_addlinkedsrvlogin 'LinkName', 'false', null, _
'SQL_UserName', 'SQL_Password'
Once, the Linked Server Setup is completed for all servers, you can check the connectivity using the query given below:
select * from OPENQUERY ( LinkName ,
'select top 1 * from sysobjects with (nolock) order by 1 desc' )
In the above code, you will have to replace the below string with values at your end:
LinkName - Is any name referring to Linked Server, it can also be the same as Linked Server Name! ServerIP_OR_NAME - Is the Name or IP address of SQL Server. SQL_UserName - Is valid Sql User on Linked server, which has rights to query the DB. SQL_Password - Guess! What...yes, you are right, it is the password.
Alert Scheduling
Once Linked servers are set up, the next job is to create a SQL Job. It will query the Linked server for Monitoring and pass on the alert to Alert Dispatcher.
A sample job supplied as part of code queries the server table every hour for any row present in it. You can reuse the sample job for setting up your own.
For maintaining a list of Alert Receiver, we will create a table which persists this information:
Create Table MonitorIP
(
IPAddress varchar(25),
Sent_flag bit,
Port int
)
Insert into MonitorIP values
('IP_WHERE_ALERT_RECEIVER_WILL_BE_RUNNING', 1, 1002)
Insert into MonitorIP values
('IP_WHERE_ALERT_RECEIVER_WILL_BE_RUNNING', 1, 1002)
Below is a sample SQL logic to be placed in Job for Monitoring a Table for Data presence.
Note: Your SQL Query could be different than this.
This query will be executed on Linked Server when the Job is fired as per the schedule. This SQL Query does 2 things:
- It queries the Linked Server and gets the Data from it.
- It check for row count greater than one. If found, then it dispatches the alert to all receivers with the help of AlertDispatcher.exe.
Declare @Row_Count int
Declare @ExePath varchar(255), @varMsg varchar(255), @varCmd varchar(2000)
Declare @IPAddress varchar(25), @Port varchar(10)
Set @ExePath = 'C:\Monitoring\AlertDispatcher.exe'
select @Row_Count = Row_Count from OpenQuery( LinkName,
'
Select count(*) as Row_Count from Your_Database..Your_Tables with _
(nolock) where Your_Columns = ''SOMEVALUE''
')
Set @varMsg = 'Date : ' + CAST(GETDATE() as varchar(50)) + ', _
Alert for Your_Database..Your_Tables on Your_Server = _
' + CAST(Row_Count as varchar(10))
IF @Row_Count > 0
BEGIN
Declare C1 cursor For select IPAddress, Port from MonitorIP where sent_flag = 1
Open C1
Fetch Next From C1 InTo @IPAddress, @Port
While @@Fetch_Status <>-1
Begin
set @varCmd = @ExePath + ' ' + @IPAddress + ' ' + _
@Port + ' "' + @varMsg + '"'
exec master..xp_cmdshell @varCmd
Fetch Next From C1 InTo @IPAddress, @Port
End
Close C1
Deallocate C1
END
Note: Don't forget to replace the @ExePath variable in the above code with Path as per your environment.
Alert Dispatcher
It is a simple console based socket client which sends the Alert message to the listening socket Server. This utility accepts the below command line parameter to send the message:
- IP Address / Machine Name
- TCP Port
- Message to be dispatched. Remember to include this between quotes(") for message containing spaces.
AlertDispatcher.exe can be executed as:
AlertDispatcher.exe localhost 1002 "DateTime, Test Message from AlertDispatcher"
Alert Receiver
It is an MFC dialog based socket application which displays the Alert send by AlertDispatcher.
This utility accepts the Port number as command line parameter to listen for incoming message from Alert Dispatcher. In case it is not supplied, default Port number is 1002.
It expects alert message to be in format "DateTime, Alert Message",
i.e. DateTime and Message text is separated by comma.
Sample Output of Alert Receiver
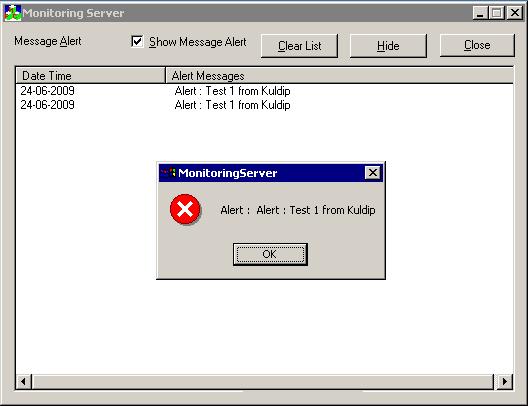
Above Output
Finally, all objects are setup correctly. Now, it is a matter of creating a new job for adding alert. Also, the existing job can be temporarily disabled by just disabling the concerned SQL Job.
Special thanks to my colleague, Chaitanya Shah who coded the Alert Dispatcher executable.
History
- 24th June, 2009: Initial post
