Introduction
In this article we will discuss about securing user passwords by using hashing and salting
on user passwords. We will first discuss about the theory of hashing and salting.
We will then try to implement a simple library that can be used to perform hashing and salting.
Background
I have seen many ASP.NET beginners making the mistake of storing the password as plain text
in the database. The first question I ask them is why are they not using the ASP.NET Roles and
Membership database and API. In most cases using the default Roles and Membership API will fulfill
the needs of the application. In some cases the application really needs to have its own tables to
save user credentials. All the applications where custom forms authentication is being used
are probably storing user credentials in the application database in some application specific schema.
Note: Please refer these two articles to learn more about custom forms authentication:
- Understanding and Implementing ASP.NET Custom Forms Authentication[^]
- A Beginner's Tutorial on Custom Forms Authentication in ASP.NET MVC Application[^]
Passwords as Plain Text
For all scenarios where we need to store user credentials in application tables, storing
the password in plain text is never a good idea. Anyone who has access to the database can easily get
to know the password of all the users. Also, even a small part of application that is prone to SQL injection
can reveal the password of all users. So what could be done to prevent this and store the password in a better way?
Storing Encrypted Passwords
Encryption is the process of encoding the message in such a way that even if anyone get hold of the message, he should
not be able to interpret anything from it. To encrypt a message we need two things. First we need an encryption
algorithm and second we need a key which will be used for encryption.
So if the requirement is not to store the password in plain text then the First thought is to keep the passwords
encrypted rather than as plain text. Well this approach is better
than storing the passwords in plain text but it still has the some problem. If someone knows the encryption
algorithm and the secret key that was used for encryption then he could decrypt the passwords easily.
Hashing - Storing Password Hashes
Hashing is the process of generating a number or a unique string for a larger string message. The hash for every
string message should be unique and there is no way the original message can be reproduced from its hash value.
No matter how strong our encryption mechanism is, there is always a possibility of regenerating the original
password if the algorithm and the secret key is known. So the even better approach would be to store the password
hashes in the table. This way there is no way to regenerate the password from the hash. Whenever the user tries to
log in, we will generate the hash for the password using the same hashing algorithm and then compare it with the hash
stored in the database to check whether the password is correct or not.
Now this approach is a lot better than storing the password in encrypted form. But this also has few limitations.
To understand the limitation let us look at the following example:
| User | Password | Hash |
| user1 | one | 1234 |
| user2 | two | 2345 |
| user3 | three | 3456 |
| user4 | one | 1234 |
| user5 | two | 2345 |
The above table shows some dummy data where 5 users have chosen there passwords and there corresponding hash values have
been generated to store in the database. Now from this table we can clearly see the limitation associated with saving the hashed password.
The problem here is that the
The above table shows some dummy data where 5 users have chosen there passwords and there corresponding hash values have
been generated to store in the database. Now from this table we can clearly see the limitation associated with saving the hashed password.
The problem here is that the user1 and user4 choose the same password and thus their generated password hash is also same. Same is the case
with user2 and user5. So if I get hold of these password hashes and I know the password of user1, I actually know the password of all
the users whose hash value is same as the hash value of user1's password.
Now this problem is less severe than the problem associated with the earlier approaches. But could we not device a technique which
will store provide us all the benefits of hashing and will also remove the limitations associated with it. The answer to this is salting and hashing.
Salting and Hashing of Passwords
Salting is a technique in which we add a random string to the user entered password and then hash the resulting string.
So even if two people have chosen the same password, the salt for them will be different. So there will never be case when the
hash for two users will be same even if they choose the same password. Following table will illustrate the concept in more details.
| User | Password
| Random Salt | Resultant Password String | Hash
|
| user1 | one
| 12 | one12 | 1234
|
| user2 | two
| 23 | two23 | 2345
|
| user3 | three
| 34 | three34 | 3456
|
| user4 | one
| 45 | one45 | 4567
|
| user5 | two
| 56 | two56 | 5678
|
Now if we look at the above table we can see that even though the user1 and user4 has chosen same password their salt value
is different and thus the resultant hash value is also different. Now the important thing to note in this approach is that
the salt value should always be random and secondly this should also be stored in the database so that it can be used while
comparing the user entered password.
Using the code
Now we have seen the theory associated with the password hashing and salting and why is this technique preferred over saving
plain text passwords, encrypted passwords or even saving password hashes. Now let us see how we can implement this salting and hashing
in in .NET so that it can be used by the applications like ASP.NET or ASP.NET MVC websites during custom forms authentication.
Let us start with the salt creation process. We need to generate a random number, for this we can use RNGCryptoServiceProvider class.
This class ensures that the generated number is always random and unique. So let us implement a simple class which will generate a random number
using this RNGCryptoServiceProvider.
public static class SaltGenerator
{
private static RNGCryptoServiceProvider m_cryptoServiceProvider = null;
private const int SALT_SIZE = 24;
static SaltGenerator()
{
m_cryptoServiceProvider = new RNGCryptoServiceProvider();
}
public static string GetSaltString()
{
byte[] saltBytes = new byte[SALT_SIZE];
m_cryptoServiceProvider.GetNonZeroBytes(saltBytes);
string saltString = Utility.GetString(saltBytes);
return saltString;
}
}
Now we have a class that will generate the random salt value for us. Let us now create a class that will take care of hashing a message.
We will use SHA256CryptoServiceProvider class to generate the hash. There are quite a few algorithms that we can choose from. Let us see
how a hash value can be generated for a string message.
public class HashComputer
{
public string GetPasswordHashAndSalt(string message)
{
SHA256 sha = new SHA256CryptoServiceProvider();
byte[] dataBytes = Utility.GetBytes(message);
byte[] resultBytes = sha.ComputeHash(dataBytes);
return Utility.GetString(resultBytes);
}
}
Now we have two classes with us:
SaltGenerator: This class' responsibility is to generate a random and unique salt every time.HashComputer: This class' responsibility is to generate the SHA256 hash value for a given string message.
Now let us look at the salting and hashing process in form of algorithm.
User creation process:
- User enters a password.
- A random salt value is generated for the user.
- The salt value is added to the password and a final string is generated.
- The hash for the final string is calculated.
- The hash and the salt is stored in the database for this user.
User tries to log in:
- User enters his user ID.
- The user is used to retrieve the users password hash and salt stored in the database.
- The user enters his password.
- The retrieved salt is added to this password and a final string is generated.
- The hash for the final string is calculated.
- This calculated hash is compared with the hash value retrieved from the database.
- If it matches the password is correct otherwise not.
So let us create a facade class on top of these two classes which will do the major portion of these activities. it will
take the users' id and password and then will take care of doing the rest. It will return the hash and salt to the user. In case
of password retrieval, it will ask the user its password and salt and then checks if it matches or not.
public class PasswordManager
{
HashComputer m_hashComputer = new HashComputer();
public string GeneratePasswordHash(string plainTextPassword, out string salt)
{
salt = SaltGenerator.GetSaltString();
string finalString = plainTextPassword + salt;
return m_hashComputer.GetPasswordHashAndSalt(finalString);
}
public bool IsPasswordMatch(string password, string salt, string hash)
{
string finalString = password + salt;
return hash == m_hashComputer.GetPasswordHashAndSalt(finalString);
}
}
Now we have a simple class library ready which is capable of salting and hashing the user passwords. using this library and
saving the values in the database will be the applications responsibility. The class diagram of this class library looks like:
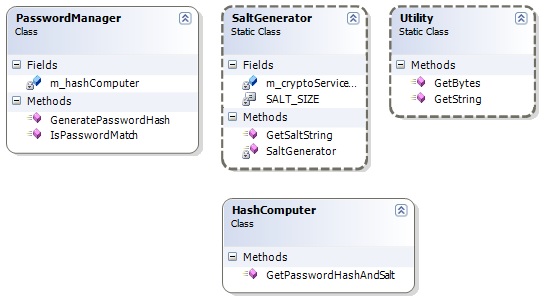
Note: The Utility class contains 2 simple methods to convert string to byte[] and vice-verse.
Creating a Test Application
Let us now go ahead a create a simple test application to test this library. Let us create a simple console application. Let us first create
a Model class that will hold the user login data.
class User
{
public string UserId { get; set; }
public string PasswordHash { get; set; }
public string Salt { get; set; }
}
Note: This is a very rudimentary model for User login details. It is created only to explain the concepts of the article.
Real world application will contain more detailed model.
This model class represent a user details for any user from the user login details table. We will use this model while creating
a new user and while the user tries to log in.
Now let us try to simulate/mock the database functionality. let us create a simple repository class which will keep all the data in
memory rather than pushing them to the database. The real repository class should push the data into the database in the respective
operations.
class MockUserRepository
{
List<user> users = new List<user>();
public void AddUser(User user)
{
users.Add(user);
}
public User GetUser(string userid)
{
return users.Single(u => u.UserId == userid);
}
}
And finally let us write some code to simulate and test the user creation and password comparison functionality.
class Program
{
static MockUserRepository userRepo = new MockUserRepository();
static PasswordManager pwdManager = new PasswordManager();
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string salt = SimulateUserCreation();
SimulateLogin(salt);
Console.ReadLine();
}
public static string SimulateUserCreation()
{
Console.WriteLine("Let us first test the password hash creation i.e. User creation");
Console.WriteLine("Please enter user id");
string userid = Console.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine("Please enter password");
string password = Console.ReadLine();
string salt = null;
string passwordHash = pwdManager.GeneratePasswordHash(password, out salt);
User user = new User
{
UserId = userid,
PasswordHash = passwordHash,
Salt = salt
};
userRepo.AddUser(user);
return salt;
}
public static void SimulateLogin(string salt)
{
Console.WriteLine("Now let is simulate the password comparison");
Console.WriteLine("Please enter user id");
string userid = Console.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine("Please enter password");
string password = Console.ReadLine();
User user2 = userRepo.GetUser(userid);
bool result = pwdManager.IsPasswordMatch(password, user2.Salt, user2.PasswordHash);
if (result == true)
{
Console.WriteLine("Password Matched");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Password not Matched");
}
}
}
Let us now try to create a user and then enter a valid password:

And let us now try to check with wrong password once:

And so we have seen the basics of password salting and hashing and have created a simple reusable class library that can be used to create achieve this.
Point of interest
In this article we have discussed the recommended way to saving the user passwords by using salting and hashing on
user passwords. We have created a simple reusable class library that can be used to generate the salt and hashes user passwords.
I really recommend using this technique whenever we are using custom forms authentication.
This article has been written from a beginner's perspective. I Hope this has been informative.
History
- 19 June 2013: First version.
