Introduction
A data access layer can be an important part of a software application. Applications almost always need access to data and we should design a separate layer for this purpose. Now we want to use the generics in C# and design a really powerful data access layer for use in all applications without requiring any changes. For more information about Generics in C#, you can follow one of these links:
Of course, it should be noted that all of these ideas have been implemented in the Entity Framework in the best possible way, but the problem is that the Entity Framework an not to be used with the some DBMS same as MS Access. And the other hand is aimed at showing the power of generics and facilities in programming.
Background
After reading the current version of this article, you can read the new version from here. In the new version, I solved some problems which are the same as SQL injection and multiple database support.
Data Access Layer Overview
In this article, we introduce our data access layer architect (follow the below picture). As you see in the picture, we have two top level namespaces, Model and DataAccessHandler, Model is a class view of database and DataAccessHandler is a wrapper for the ADO.NET to the building communication with DBMS.
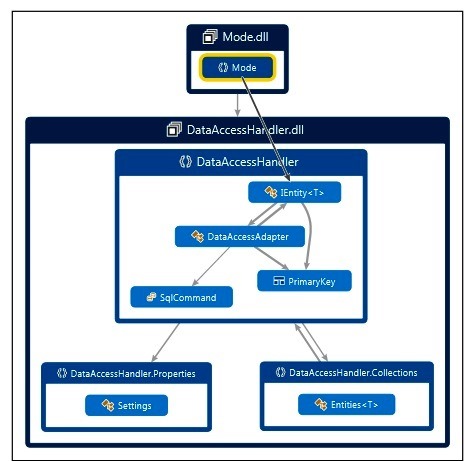
Model
Each table in our database should have an implemented class in Model with the same field names and field data types. Pay attention that each class must inherit from IEntity (see the below picture). For example in this sample, Personnel is a class view of tblPersonnel in database and it is inherited from IEntity.

Context
Context is implemented with singleton design pattern as a model container, using this container to insert, update and delete the entities makes Collections synchronized with the database. Thus the changes are not required to update the Collections again and it can reduce a cost of data access layer. Insert, Update and Delete methods in IEntity are implemented to consider this requirement. Please pay attention to the following codes:

public void AddPersonel(Mode.Personnel personnel)
{
Mode.Context.Instance.Personnel.Insert(personnel);
}
public void UpadtePersonel(Mode.Personnel personnel)
{
Mode.Context.Instance.Personnel.Update(personnel);
}
public void RemovePersonel(Mode.Personnel personnel)
{
Mode.Context.Instance.Personnel.Delete(personnel);
}
DataAccessHandler
In this project, our top level name space is DataAccessHandler so this container has DataAccessAdapter, IEntity, Entities, SqlCommand enumerator and PrimaryKey data-structure.
| Class | Description | Namespace |
IEntity | It is an interface for our entities in entity model. For example, if we want the use of this DAL in our Personnel Management System, the personnel object is a target entity that should implement this interface. Each entity contains a method to insert and update and remove a collection of its own, if it will be inherited from IEntity. | DataAccessHandler |
Entities | It is a collection of entities, this is a generic list and can be really useful for us, so each entity has its own list. | DataAccessHandler.Collection |
PrimaryKey | This property is used to specify primary key for each entity. it is a structure with two element Name and Value, Name is a primary key name and value is a primary key value | DataAccessHandler.IEntity |
DataAccessAdapter | It is a wrapper to the working with ADO.NET objects, so we expect this object to communicate with our database. (Execute the sql commands same as insert, update, delete and select on the target database). This object is to do your job that requires a sqlcommand enumerator. | DataAccessHandler |
SqlCommand | This is an enumerator object and is used to specify our DAL SQL command to transact with database. | DataAccessHandler |
| | |

DataAccessAdapter Backbone Methods
Initialize Method
This method is used to initialize DataAccessAdapter connection string and password for connecting to the database. We used this method only once.
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region Initialize DataAccessAdapter
string datasource = @"../../../Testdb.mdb";
string password = "";
DataAccessHandler.DataAccessAdapter.Initialize(datasource, password);
#endregion
}
DoEntity<T> Method
This method is a generic method and has 3 parameters, the first parameter gets the entity and the second parameter gets the sqlCommand (Insert, Update, Delete, or Select), finally, the third parameter gets the where condition, however it is not necessary and usually used with Update, Delete or Select commands. For example, see the Insert method of IEntity class:
public virtual bool Insert(T entity)
{
bool result = DataAccessAdapter.DoEntity(entity, SqlCommand.Insert, "");
if (result)
Collection.Add(entity);
return result;
}
GenerateCommand <T> Method
This method is a generic method and is the same as DoEntity method which has 3 parameters too. But this method should be decided about sqlCommand, if the sqlCommand is an insert, it should be called InsertCommand and if it is an update command, it should be called UpdateCommand, etc.
public static string GenerateCommand<T>(SqlCommand sqlCommand,T entity,
string where = " ")where T:IEntity<T>
{
string commandText = string.Empty;
switch (sqlCommand)
{
case SqlCommand.Insert:
commandText = InsertCommand(entity);
break;
case SqlCommand.Update:
if(where == "")
commandText = UpdateCommand(entity);
else if(where != "")
commandText = UpdateCommand(entity, where);
break;
case SqlCommand.Select:
if (where == "")
commandText = selectCommand(entity);
else if (where != "")
commandText = selectCommand(entity, where);
break;
case SqlCommand.Delete:
if (where == "")
commandText = deleteCommand(entity);
else if (where != "")
commandText = deleteCommand(entity, where);
break;
default:
break;
}
return commandText;
}
InsertCommand
In this method, we should generate SQL Insert command for entity parameter, _perfix and _suffix are used when the entity table name in database has prefix or suffix same as tblPersonel. The most important part of this method is GetInfo function, other methods (Update, Delete, Select) are similar to this method so we don't explain these methods.
private static string InsertCommand<T>(T entity) where T:Entity<T>
{
string Insert = "INSERT INTO " + _perfix + ((Entity<T>)entity).EntityName + _suffix;
string columns = "(";
string values = "VALUES(";
Dictionary<string, object> infos = GetInfo(entity);
foreach (var item in infos)
{
if (item.Value != null && item.Value != "" &&
!entity.PrimaryKey.Exists(p => p.Name == item.Key))
{
columns += item.Key + ",";
values += Formatting(item.Value.ToString()) + ",";
}
}
columns = columns.Remove(columns.Length - 1, 1)+") ";
values = values.Remove(values.Length - 1, 1) +") ";
Insert += columns + values;
return Insert;
}
GetInfo Method
This method used Reflection in .NET library for getting properties of entities in Model, we remind each table in database has a class in the Model called entity so what I mean when I say, getting properties of entities is properties of classes in the Model. At the end of this code, you can see properties of Personnel entity in this sample.
Note: The Primary-key of entity is marked with this attribute [DataObjectFieldAttribute(true, true, false)]
namespace Mode
{
public class Personnel:DataAccessHandler.IEntity<Personnel>
{
#region Table Fields
int _id;
[DisplayName("Identity")]
[Category("Column")]
[DataObjectFieldAttribute(true, true, false)]
public int ID
{
get { return _id; }
set { _id = value; }
}
string _fName;
[DisplayName("First Name")]
[Category("Column")]
public string FName
{
get { return _fName; }
set { _fName = value; }
}
string _lName;
[DisplayName("Last Name")]
[Category("Column")]
public string LName
{
get { return _lName; }
set { _lName = value; }
}
#endregion
#region Initialize
public Personnel() { }
#endregion
}
}
Another important note about this method are the conditions. The first condition checks the item is the property or not and the second condition checks the item is readable, is serializable and accessible follow of access modifier or no and the final condition removes the PrimaryKey and EntityName at this scenario !! Why? Think about it. 
public static Dictionary<string, object> GetInfo<T>(T entity) where T : IEntity<T>
{
try
{
Dictionary<string, object> values = new Dictionary<string, object>();
foreach (var item in ((IEntity<T>)entity).GetType().GetProperties())
{
if (item.MemberType == System.Reflection.MemberTypes.Property)
{
if (item.CanRead && item.PropertyType.IsSerializable && item.PropertyType.IsPublic)
{
if (item.Name == "PrimaryKey" || item.Name == "EntityName")
continue;
else if (item.PropertyType.IsEnum)
values.Add(item.Name, item.GetValue(entity, null).GetHashCode());
else
values.Add(item.Name, item.GetValue(entity, null));
}
}
}
IsSqlInjection(values);
return values;
}
catch (Exception)
{
throw;
}
}
What is IsSqlInjection() Method
For answering this question, we should answer what are SQL injection attacks but I prefer to redirect you here for getting more information about it. So this method prevents them, however I know it is not a really secure method for this purpose but we can improve it and I create it for development in future.
internal static void IsSqlInjection(Dictionary<string,object> source)
{
foreach (var item in source)
{
if (item.Value != null)
if (item.Value.ToString().Contains('@') || item.Value.ToString().Contains('=') ||
item.Value.ToString().Contains("'"))
throw new Exception("It is not secure using");
}
}
IEntity<T> Interface
IEntity<T> is a generic interface for the entities in the model. Each entity from the model can be inherited from IEntity<T> and IEntity<T> has some basic methods same as Insert, Update, Delete, Select and Load. In the following, we will review IEntity<T> methods sequence diagram.
Update Method Sequence Diagram

Insert Method Sequence Diagram

Delete Method Sequence Diagram

I hope that will be useful...
This topic has been extended in the next part..
History
- 13th August, 2013: Revision
- 16th August, 2013: Revision
