Color Constancy
Color constancy is a mechanism of detection of color independent of light source.
The light source many introduce color casts in captured digital images
To solve the color constancy problem a standard method is to estimate the color of the prevailing light
and then, at the second stage, remove it.
Once the color of light in individual channels is obtained the each color pixel is normalized by a scaling factor .
Two of the most commonly used simple techniques for estimating the color of the light are the Grey-World and Max-RGB algorithms.
These two methods will work well in practice if the average scene color is gray or the maximum is white.
Gray world assumption
The Gray World Assumption is a white balance method that assumes that your scene, on average, is a neutral gray.
Gray-world assumption hold if we have a good distribution of colors in the scene.
Assuming that we have a good distribution of colors in our scene,the average reflected color is assumed to be the color of the light.
Therefore, we can estimate the illumination color cast by looking at the average color and comparing it to gray.
Gray world algorithm produces an estimate of illumination by computing the mean of each channel of the image.
One of the methods of normalization is that the mean of the three components is used as illumination estimate of the image.
To normalize the image of channel i ,the pixel value is scaled by

where
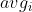
is the channel mean
and

$ is the illumination estimate .
Another method of normalization is normalizing to the maximum channel by scaling by $s_i$
}{avg_i})
Another method of normalization is normalizing to the maximum channel by scaling by norm $m_i$
} )
}{m_i}) Example 1.1:gray world (original,norm m1,norm m2,norm m3)
Example 1.2:gray world (original,norm m1,norm m2,norm m3)
Example 1.3:gray world (original,norm m1,norm m2,norm m3)
Example 1.4:gray world (original,norm m1,norm m2,norm m3)
Example 1.4:gray world
Example 1.5:gray world
Example 1.5:gray world
Example 1.6:gray world
Example 1.7:gray world
Example 1.8:gray world
Example 1.9:gray world
Example 1.10:gray world
Example 1.1:gray world (original,norm m1,norm m2,norm m3)
Example 1.2:gray world (original,norm m1,norm m2,norm m3)
Example 1.3:gray world (original,norm m1,norm m2,norm m3)
Example 1.4:gray world (original,norm m1,norm m2,norm m3)
Example 1.4:gray world
Example 1.5:gray world
Example 1.5:gray world
Example 1.6:gray world
Example 1.7:gray world
Example 1.8:gray world
Example 1.9:gray world
Example 1.10:gray world
Some of the images are taken from
http://research.edm.uhasselt.be/~oancuti/Underwater_CVPR_2012/ image set
Code
For code refer to site
https://github.com/pi19404/m19404/tree/master/ColorConstancy/
The files are color_constancy.cpp and color_constancy.hpp.
The class for performing gray world transformation is gray_world.
Mat run2(Mat,int p,int m);
The norm factor is

for gray world algorithm and various normalization techniques can be passed
as
)
