Introduction
This article demos a sample WPF application that consumes Bing Maps web service that comes handy if your business requirements indicate that you need to build a desktop application. This article demonstrates using the Geocode, Imagery, Route, and Search services of the Bing Maps Web Services in a desktop application, using Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF) and C#.
Background
Ever wish to have bing maps integrated with your Windows application? Here is the solution. All you need is Visual Studio 2008, .NET Framework 3.0 and Bing Maps Platform Developer Account credentials. You can sign up for a free developer account at the Bing Maps Account Center. The Bing Maps Web Services require that you have a Bing maps key to make requests. You can create a key when you sign into your account at Bing Maps Account Center. For more information about creating a key, see Accessing the Bing Maps Web Services.
Using the Code
Once you have your Bing Maps Account and the key, you are ready to start creating proxy classes that reference the Bing Maps Web Services. To do this, you need to set up service references which provide the geocoding, mapping and search features. These are added as Windows Communication Foundation (WCF) services and Visual Studio builds proxy files for the project.
The code is simple. The first thing you have to do before calling any method of these services is to set the key that you got from your bing maps account. Once done, you create an instance of service that you want to use and try to identify the method that you want to invoke. Generally the methods need object of some type to be passed as its param, so spend some time understanding the param and what properties need to be set.
You will notice that the app has 6 buttons. Here is what each button does:
1. GeoCode
This button converts a postal address into geo code (longitudes and latitudes). This feature is based on Geocode Service. The Geocode Service offers methods to geocode addresses and reverse geocode locations.
Here is the code that explains how to get the geo code for the specified address. It is very simple. First, start by setting the key that you got from your bing maps account as the credential for GeocodeRequest. Next, set the filters. Once done, create the instance of GeoServiceClient and fire its GeoCode method.
private GeocodeResponse GeocodeAddressGeocodeResponse(string address)
{
GeocodeRequest geocodeRequest = new GeocodeRequest()
geocodeRequest.Credentials = new GeocodeService.Credentials();
geocodeRequest.Credentials.ApplicationId = key;
geocodeRequest.Query = address;
ConfidenceFilter[] filters = new ConfidenceFilter[1];
filters[0] = new ConfidenceFilter();
filters[0].MinimumConfidence = GeocodeService.Confidence.High;
GeocodeOptions geocodeOptions = new GeocodeOptions();
geocodeOptions.Filters = filters;
geocodeRequest.Options = geocodeOptions;
GeocodeServiceClient geocodeService = new GeocodeServiceClient();
GeocodeResponse geocodeResponse = geocodeService.Geocode(geocodeRequest);
return geocodeResponse;
}
Here is a screen shot:
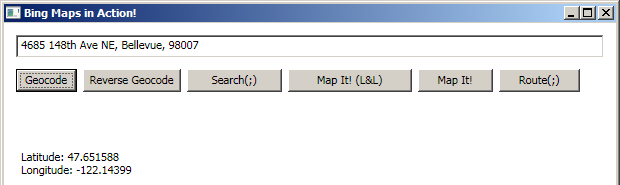
2. Reverse GeoCode
As the name suggests, you can convert the geo code into readable postal address. It is quite similar to Get GeoCode method explained above.
3. Search
This method takes the "what" and "where" part of the query. "What" is things like gas stations, barber, etc. and "where" is the location. It returns a list of search results. The app shows the name and distance, but you could do more with the data received.
Here is the code snippet that gets the search results near the location specified.
private string SearchKeywordLocation(string keywordLocation)
{
String results = "";
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest();
searchRequest.Credentials = new SearchService.Credentials();
searchRequest.Credentials.ApplicationId = key;
StructuredSearchQuery ssQuery = new StructuredSearchQuery();
string[] parts = keywordLocation.Split(';');
ssQuery.Keyword = parts[0];
ssQuery.Location = parts[1];
searchRequest.StructuredQuery = ssQuery;
searchRequest.SearchOptions = new SearchOptions();
searchRequest.SearchOptions.Filters =
new FilterExpression()
{
PropertyId = 3,
CompareOperator = CompareOperator.GreaterThanOrEquals,
FilterValue = 8.16
};
SearchServiceClient searchService = new SearchServiceClient();
SearchResponse searchResponse = searchService.Search(searchRequest);
if (searchResponse.ResultSets[0].Results.Length > 0)
{
StringBuilder resultList = new StringBuilder("");
for (int i = 0; i < searchResponse.ResultSets[0].Results.Length; i++)
{
resultList.Append(String.Format("{0}. {1},
[Dist]{2}, [Loc]{3}, [Id]{4}\n", i + 1,
searchResponse.ResultSets[0].Results[i].Name,
searchResponse.ResultSets[0].Results[i].Distance,
searchResponse.ResultSets[0].Results[i].LocationData,
searchResponse.ResultSets[0].Results[i].Id));
}
results = resultList.ToString();
}
else
results = "No results found";
return results;
}
Here is the snap shot:

4. MapIt (L&L)
This method receives geo code and shows the map of that area. See #5 point below for more details.
5. MapIt
This method receives the English like address and shows the map. You will also see a scroll bar that you could use to set the zoom level.
Here is the code snippet. It is quite simple. You create an instance of Imagery Service and fire its GetMapUri method. This method will take object of MapUriRequests. This is the object where you get the longitude and latitude and the zoom level.
private string GetImagery(string locationString, int zoom)
{
MapUriRequest mapUriRequest = new MapUriRequest();
mapUriRequest.Credentials = new ImageryService.Credentials();
mapUriRequest.Credentials.ApplicationId = key;
mapUriRequest.Center = new ImageryService.Location();
string[] digits = locationString.Split(',');
mapUriRequest.Center.Latitude = double.Parse(digits[0].Trim());
mapUriRequest.Center.Longitude = double.Parse(digits[1].Trim());
MapUriOptions mapUriOptions = new MapUriOptions();
mapUriOptions.Style = MapStyle.AerialWithLabels;
mapUriOptions.ZoomLevel = zoom;
mapUriOptions.ImageSize = new ImageryService.SizeOfint();
mapUriOptions.ImageSize.Height = 200;
mapUriOptions.ImageSize.Width = 300;
mapUriRequest.Options = mapUriOptions;
ImageryServiceClient imageryService = new ImageryServiceClient();
MapUriResponse mapUriResponse = imageryService.GetMapUri(mapUriRequest);
return mapUriResponse.Uri;
}
Here is the snap shot:

6. Route
This method takes two addresses and returns the route between these two end points. The Route Service can calculate a route between waypoints. As with the other services, you need to start by creating a request object. A RouteRequest object includes the array of waypoints to route between and options on how to calculate the route. The result object contains a set of step by step instructions.
In order to get the route, you will need to use RouteService. This service needs an instance of WayPoint where you set the coordinates of start and end address. Once you are done populating the WayPoint object, just call RouteService.CalculateRoute method. Here is the code snippet:
string[] points = new string[]{start, end};
Waypoint[] waypoints = new Waypoint[points.Length];
int pointIndex = -1;
foreach (string point in points)
{
pointIndex++;
waypoints[pointIndex] = new Waypoint();
string[] digits = point.Split(',');
waypoints[pointIndex].Location = new RouteService.Location();
waypoints[pointIndex].Location.Latitude = double.Parse(digits[0].Trim());
waypoints[pointIndex].Location.Longitude = double.Parse(digits[1].Trim());
if (pointIndex == 0)
waypoints[pointIndex].Description = "Start";
else if (pointIndex == points.Length)
waypoints[pointIndex].Description = "End"
else
waypoints[pointIndex].Description =
string.Format("Stop #{0}", pointIndex);
}
routeRequest.Waypoints = waypoints;
RouteServiceClient routeService = new RouteServiceClient();
RouteResponse routeResponse = routeService.CalculateRoute(routeRequest);
Here is the snap shot:

Points of Interest
Now you know how to consume Bing Maps web Geocode, Imagery, Route, and Search services. Feel free to play with the code and dig deeper. Have fun!
History
- 13th May, 2010: Initial version
