Introduction
We would be developing a basic AngularJS application in which we would be covering following walkthroughs:
- Basics Of AngularJs
- Routing
- Using its syntax
- Interaction with Data Services
Resources:
AngularJS library can be downloaded from https://angularjs.org/.
Tutorials can be found at https://builtwith.angularjs.org
For the purpose of this tutorial, IDE used would be VS 2012, .NET MVC template.
AngularJs is a totally client side SPA (Single Page Application) MV* framework which begins its operation after the DOM is completely loaded similar to other client side libraries like JQuery. It has the following major components:
- "SPA" framework for building robust client-centric applications
- Testing – e2e integration, Unit testing
- Two-way data binding, template building, declarative UI
- Views, Controllers, Scope
- Dependency Injection, Directives, filters
- Modules and Routes
Background
Knowledge of basic JavaScript, object literal notation.
AngularJS starts its execution on load of complete DOM, then finding the various data points and replacing them with data. The following figure explains the lifecycle of Angular app.
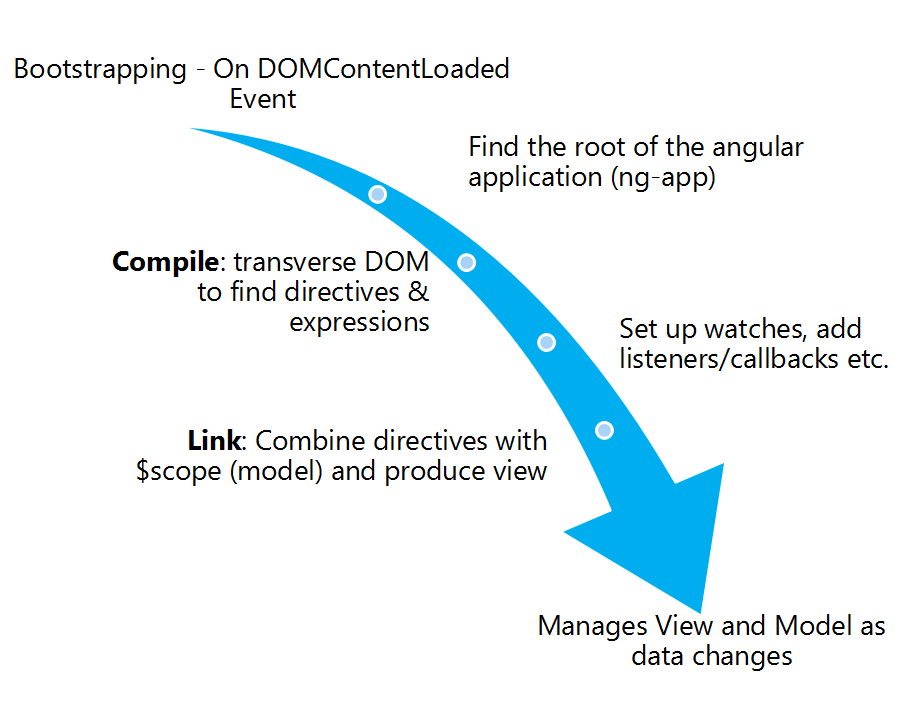
AngularJS Lifecycle
AngularJS is a framework which has the following components:

Using the Code
To set up an AngularJS application, all you require is a web server to serve your pages and AngularJS libraries.
This article would contain code for the following AngularJs components:
- Services - Used as helper functions for querying data
- Controllers - Used to provide data and write business logic
- Views - Used for presenting information
- Filters - Used as helper methods for formatting data
Server/Editors
Different editors to structure your application and act as server are available, e.g., Yeoman, Lineman, Visual Studio.
Configuring Application
So let's start the code part. I’d be using Visual Studio as the development IDE, its MVC based template to structure the code.
So AngularJs uses a set of JS files for its normal operation, routing, data services interaction, etc.
Once you setup an empty MVC template, place the files in your master/layout page so that they are available to every view that inherits this layout page.


Project Structure
Code
The execution starts from the app.js file which contains the routing logic.
The routes are defined in a pattern from specific to generic in the following manner:
.when('<Url>',{
templateUrl: '<ViewPath To Load>',
controller: '<ControllerName To Use for View>'
})
app.js File
var appModule = angular.module("appModule", ['ngRoute', 'demoControllers']);
appModule.config(['$routeProvider', function ($routeProvider) {
$routeProvider.
when('/user', {
templateUrl: 'Content/NgUser.html',
controller: 'UserController'
}).
when('/user/:userId', {
templateUrl: 'Content/NgUserDetail.html',
controller: 'MessageController'
}).
when('/message/:messageId', {
templateUrl: 'Content/NgMessageDetails.html',
controller: 'MessageDetailController'
}).
otherwise({
redirectTo: '/user'
});
}]);
Services
Since AngularJS is a client side JavaScript framework, it depends on data from services in the form of JSON primarily. It has builtIn abstractions for fetching data from remote or local service providers, e.g., @http, similar to $.ajax function in JQuery.
services.js File
var demoServices = angular.module("demoServices", []);
demoServices.factory("UserService", ["$http", "$q", function ($http, $q) {
var serv = {};
return ({
GetAllUsers: GetAllUsers,
GetUserDetail: GetUserDetail
});
function GetAllUsers() {
var req = $http({
method: "get",
url: "/service/getusers"
});
return req.then(handleSuccess, handleError);
}
function GetUserDetail(id) {
var req = $http({
method: "get",
url: "/service/GetUserDetail",
params: {
id: id
}
});
return req.then(handleSuccess, handleError);
}
function handleError(response) {
if (
!angular.isObject(response.data) ||
!response.data.message
) {
return ($q.reject("An unknown error occurred."));
}
return ($q.reject("hagjhsaggjasjgjagdj error"));
}
function handleSuccess(response) {
return (response.data);
}
}]);
Controllers
Controllers are the place to write business logic and bind data to model to be used in the view.
Each controller is injected (Dependency Injected By AJs framework) with a $scope object that contains data (properties, object and functions).
Scope(ViewModel) is the glue between Controller and View. It carries data from controller to view and back from view to controller. AngularJS supports two way data binding, changes to view updates model and changes to model updates view.

SCOPE - View Model

controllers.js File
var demoControllers = angular.module("demoControllers", ['demoServices', 'demoFilters']);
demoControllers.controller("HomeController", ["$scope", "$http", function ($scope, $http) {
$scope.pageHeading = 'this is page title.';
$http.get('/service/getmessages')
.success(function (data) {
$scope.messages = data;
})
.error(function () {
alert("some error");
});
}]);
demoControllers.controller("UserController", ["$scope", "UserService", function ($scope, UserService) {
$scope.pageHeading = 'behold the majesty of your page title';
UserService.GetAllUsers().then(function (data) {
$scope.users = data;
});
UserService.GetUserDetail(2).then(
function (data) {
$scope.users.push(data);
});
$scope.AddUser = function () {
console.log($scope.newUser.name);
console.log($scope.newUser.email);
alert("User Added");
$scope.users.push({ name: $scope.newUser.name, email: $scope.newUser.email });
$scope.newUser.name = "";
$scope.newUser.email = "";
}
}]);
View
View contains the presentation logic and data points for inserting the data from controller' $scope model.
{{<variable here>}}
Angular searches the above notation and replaces them with the data from the same named variable in $scope.
E.g.:
<code>Controller: ($scope.username = "Scott";)
View: {{ username }}.
Output: Scott.</code>
Various other directives exists like:
ng-view: Angular replaces the data from the corresponding view looking at the route inside the element containing this attribute. This attribute is used in the master page of site.ng-app: Used to define the module for a block of HTML.ng-repeat: Repeats the element similar to foreach.ng-click: Defines the function to be called onClick of element.ng-model: Two way data bind the model variable. Creates if it does not exist. Eg: ng-model="newUser.name" - It creates a variable and displays its value in the element.ng-controller: Defines a controller to be used for a scope in HTML.
Master page (_Layout.cshtml)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>AngularJS Application</title>
<link href="~/favicon.ico" rel="shortcut icon" type="image/x-icon" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width" />
@Styles.Render("~/Content/css")
@Scripts.Render("~/bundles/modernizr")
@Scripts.Render("~/bundles/jquery")
<script src="~/Scripts/Angular/angular/angular.min.js"></script>
<script src="~/Scripts/Angular/angular-route/angular-route.min.js"></script>
<script src="~/Scripts/Angular/angular-resource/angular-resource.min.js"></script>
<script src="~/Scripts/App/app.js"></script>
<script src="~/Scripts/App/controllers.js"></script>
<script src="~/Scripts/App/filters.js"></script>
<script src="~/Scripts/App/services.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<header>
</header>
<div id="body" ng-app="appModule">
<section class="content-wrapper main-content clear-fix" ng-view>
@RenderBody()
</section>
</div>
<footer>
<div class="content-wrapper">
<div class="float-left">
<p>© @DateTime.Now.Year - My ASP.NET MVC Application</p>
</div>
</div>
</footer>
@RenderSection("scripts", required: false)
</body>
</html>
ng-view attribute in master page.
NgUser.html File
Hello
<a href="#/user/">User</a>
<div class="bar">User List</div>
<div ng-repeat="us in users" style="padding: 10px;">
<a style="text-decoration: none;" href="#/user/{{us.name}}">
<b>{{$index + 1}}. </b>{{us.name}}, {{us.email}}
</a>
</div>
<div class="bar">Add A User</div>
<form name="addUserForm">
<input placeholder="username" type="text"
name="fullname" value=" " ng-model="newUser.name" required />
<input placeholder="email" type="email"
name="email" value=" " ng-model="newUser.email" required />
<button ng-click="AddUser()"
ng-disabled="!addUserForm.$valid">Click To Add User</button>
</form>
<div ng-controller="TempController">
{{pageMessage}}
Test - {{pageHeading}}
</div>
<script>
$(function () {
});
</script>
HTML form works similar to normal constructs of HTML, just that onClick of submit button, a function is called (AddUser() here) which handles validating and saving the data.
Filters
Filters are used for manipulation/formatting of the data to be presented in a view.
filters.js File
var demoFilters = angular.module("demoFilters", []);
demoFilters.filter("titleCase", function () {
var titleCaseFilt = function (input) {
var wordsInInput = input.split(' ');
for (var i = 0; i < wordsInInput.length; i++) {
wordsInInput[i] = wordsInInput[i].charAt(0).toUpperCase() + wordsInInput[i].slice(1);
}
return wordsInInput.join(' ');
};
return titleCaseFilt;
});
demoFilters.filter("searchForFilter", function () {
return function (arr, searchForText) {
if (!searchForText) {
return arr;
}
var result = [];
searchForText = searchForText.toLowerCase();
angular.forEach(arr, function (item) {
if (item &&
(item.sender
&& item.sender.toString().toLowerCase().indexOf(searchForText) !== -1)
||
(item.body
&& item.body.toString().toLowerCase().indexOf(searchForText) !== -1)
||
(item.subject
&& item.subject.toString().toLowerCase().indexOf(searchForText) !== -1)
) {
result.push(item);
}
});
return result;
};
});
Summary
So, in this article, we looked at how to develop a sample application in AngularJS. We also looked at some of the components Angular provides for modularity and abstraction.
