Introduction
Visual Studio 2010 provides the "Setup Project" template under "File/New Project/Installed Templates/Other Project Types/Setup and Deployment/Visual Studio Installer" to package files and assemblies into a Windows Installer Package (.msi file). The Setup Project defines the name, manufacturer and version of the package, where the source of the files and assemblies are, where these should be installed, what registry modifications should be done and what custom actions should run. The definition of the Setup Project is saved in a file with extension vdproj. This file is an ASCII file, and uses a JSON similar syntax. The problem is, that when modifications are done in Visual Studio on a Setup Project, Visual Studio may do some weird things. When comparing the new and the old version, it is difficult to determine if only the desired changes where made, or if Visual Studio did some arbitrary changes. The provided tool converts a .vdproj file to a .p.xml file that lists the folders and files in alphabetical order. When comparing the new and old version of the .p.xml file, it is easy to determine if only the desired changes were made.
Code Description
This project uses the code of VDProjectXML on GitHub. That project converts 1:1 a .vdproj file to a .xml file and vice versa. In this project, that code was converted from C# to VB.NET and an additional XML file is generated which lists the folders and files alphabetically.
Projects
The provided source has two folders:
- VDProjXML: The tool that converts a .vdproj file to two .xml files:
- .xml: a 1:1 representation of the .vdproj
- .p.xml: an XML file containing the folders and files in alphabetical order
- Demo
ClassLibrary1: assembly put into GAC, used by ConsoleApplication1ClassLibrary2: assembly put into GAC, used by ConsoleApplication2ConsoleApplication1: a console application using ClassLibrary1, writing a hello messageConsoleApplication2: a console application using ClassLibrary1, writing a hello messageSetup1v1: version 1 of a setup project containing ClassLibrary1 and ConsoleApplication1Setup1v2: version 2 of previous setup project containing additionally ClassLibrary2 and ConsoleApplication2
VDProj Syntax
It is easier to explain the syntax of the Setup Project file when it has been converted to XML. To understand the text, you might want to open the file Setup1v1\Setup1.xml. The Setup Project files have the element DeployProject/Deployable/File:
<deployproject>
...
<Deployable>
...
<File>
This element contains an element for each file. For example, for ConsoleApplication1.exe:
<_x007b_9f6f8455-1ef1-4b85-886a-4223bcc8e7f7_x007d__x003a__1d474339abbb4af1b32224edb2841e26>
<AssemblyRegister valueType="3" value="1" />
<AssemblyIsInGAC valueType="11" value="FALSE" />
<AssemblyAsmDisplayName valueType="8" value="ConsoleApplication1,
Version=1.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, processorArchitecture=x86" />
<ScatterAssemblies>
<_1D474339ABBB4AF1B32224EDB2841E26>
<Name valueType="8" value="ConsoleApplication1.exe" />
<Attributes valueType="3" value="512" />
</_1D474339ABBB4AF1B32224EDB2841E26>
</ScatterAssemblies>
<SourcePath valueType="8"
value="..\ConsoleApplication1\bin\Release\ConsoleApplication1.exe" />
<TargetName valueType="8" value="" />
<Tag valueType="8" value="" />
<Folder valueType="8" value="_4150DEBE0E5B4CF79CB533E65291044A" />
<Condition valueType="8" value="" />
<Transitive valueType="11" value="FALSE" />
<Vital valueType="11" value="TRUE" />
<ReadOnly valueType="11" value="FALSE" />
<Hidden valueType="11" value="FALSE" />
<System valueType="11" value="FALSE" />
<Permanent valueType="11" value="FALSE" />
<SharedLegacy valueType="11" value="FALSE" />
<PackageAs valueType="3" value="1" />
<Register valueType="3" value="1" />
<Exclude valueType="11" value="FALSE" />
<IsDependency valueType="11" value="FALSE" />
<IsolateTo valueType="8" value="" />
</_x007b_9f6f8455-1ef1-4b85-886a-4223bcc8e7f7_x007d__x003a__1d474339abbb4af1b32224edb2841e26>
This element contains an element folder, which has the value "_4150DEBE0E5B4CF79CB533E65291044A". To find the name of this folder, one has to search an element under the element DeployProject/Deployable/Folder that ends with that value:
<_x007b_3c67513d-01dd-4637-8a68-80971eb9504f_x007d__x003a__4150debe0e5b4cf79cb533e65291044a>
<DefaultLocation valueType="8"
value="[ProgramFilesFolder][Manufacturer]\[ProductName]" />
<Name valueType="8" value="#1925" />
<AlwaysCreate valueType="11" value="FALSE" />
<Condition valueType="8" value="" />
<Transitive valueType="11" value="FALSE" />
<Property valueType="8" value="TARGETDIR" />
<Folders> </Folders>
</_x007b_3c67513d-01dd-4637-8a68-80971eb9504f_x007d__x003a__4150debe0e5b4cf79cb533e65291044a>
This means, that ConsoleApplication1.exe is installed in the TARGETDIR folder, which by default will be C:\Program Files\Manufacturer1\Setup1. The Folder element contains an element Folder which may contain elements, that contain non empty Folders elements. Therefore, the whole hierarchy must be searched to find the desired folder. You may do the same exercise for ClassLibrary1 and you will find that it is installed in the folder _9EDD3CBEB70C42E0ABBF0D0D28BBBC27 which is the GAC folder.
VDProjXML
VDProjXML is the tool that converts vdproj files to XML files. It is a console application with just one module. The methods are explained here.
Main
The first command line argument contains the input filename, and the second optional command line argument contains the output filename. If the second argument is not provided, the output filename is constructed from the input filename by changing the extension. When the input filename's extension is ".vdproj", the ConvertVDProjToPXml method is called, when the input filename's extension is ".xml" the ConvertXmlVDProj method is called.
Select Case Path.GetExtension(inputFile).Trim().ToLowerInvariant()
Case ".vdproj"
ConvertVDProjToPXml(inputFile, outputFile)
Case ".xml"
ConvertXmlVDProj(inputFile, outputFile)
Case Else
Throw New Exception("Unknown file type: " & inputFile)
End Select
ConvertVDProjToPXml
This method builds a 1:1 XML representation of the vdproj file by calling the method ConvertVDProjToXmlString and saves it to a file. Then the ConvertVDProjNodeToPXml method is called, to generate an XML document that lists the files alphabetically. This XML document is saved with the extension .p.xml.
Dim xmlString As String = ConvertVDProjToXmlString(vdrpojFile)
File.WriteAllText(xmlFile, xmlString)
Console.WriteLine(xmlFile & " created")
Dim xdoc1 As New XmlDocument()
xdoc1.LoadXml(xmlString)
Dim xdoc2 As New XmlDocument()
Dim node2 As XmlElement = xdoc2.CreateElement(xdoc1.DocumentElement.Name)
xdoc2.AppendChild(node2)
ConvertVDProjNodeToPXml(xdoc1.DocumentElement, node2)
xmlFile = Path.ChangeExtension(xmlFile, ".p.xml")
xdoc2.Save(xmlFile)
ConvertVDProjToXmlString
This method converts a vdproj file to XML with a 1:1 mapping. It is the translation to VB.NET of the code in VDProjectXML on GitHub.
ConvertVDProjNodeToPXml
This method loops recursively over all elements in a vdproj file and copies them to a new XML document. The elements "Hierarchy", "File", and "Folder" are excluded. For the "Folder" element, a special mapping is done by calling ConvertFolderList.
Dim excludeNodes As String() = {"Hierarchy", "File", "Folder"}
Dim xdoc2 As XmlDocument = XmlNodeGetDocument(containerNode2)
For Each node1 As XmlNode In containerNode1.ChildNodes
If Array.IndexOf(excludeNodes, node1.Name) < 0 Then
Dim node2 As XmlElement = xdoc2.CreateElement(node1.Name)
For Each attr1 As XmlAttribute In node1.Attributes
node2.SetAttribute(attr1.Name, attr1.Value)
Next
containerNode2.AppendChild(node2)
ConvertVDProjNodeToPXml(node1, node2)
ElseIf node1.Name = "Folder" Then
ConvertFolderList(containerNode1, containerNode2)
End If
Next
ConvertFolderList
The ConvertFolderList method loops recursively over the Folder and Folders elements. For each Folder element found, a Folder element is constructed in the new XML document. The folderId is extracted from the element name by taking the portion between the last underscore and the end of the name. The elements "Name", "Property", "AlwaysCreate", "DefaultLocation" of the Folder element have the attribute "value". These elements are made attributes in the new Folder element. The folderId is searched in the elements under the "File" element. The file elements found are ordered by their SourcePath's element. A File element is created in the new XML document and placed under the Folder element. A File element has the elements "SourcePath", "Exclude", "IsDependency" which are made attributes in the new File element.
Private Sub ConvertFolderList(folderContainerNode1 As XmlNode, folderContainerNode2 As XmlNode)
Dim folderPattern As String = "Folders/*"
If folderContainerNode1.Name = "Deployable" Then
folderPattern = "Folder/*"
End If
Dim folderList1 As XmlNodeList = folderContainerNode1.SelectNodes(folderPattern)
If folderList1.Count > 0 Then
Dim xdoc1 As XmlDocument = folderContainerNode1.OwnerDocument
Dim xdoc2 As XmlDocument = XmlNodeGetDocument(folderContainerNode2)
Dim foldersNode2 As XmlNode = folderContainerNode2.AppendChild(xdoc2.CreateElement("Folders"))
Dim folderEnumerable1 As System.Linq.IOrderedEnumerable(Of XmlNode) =
folderList1.Cast(Of XmlNode)().OrderBy(Function(n) _
n.SelectSingleNode("Name/@value").Value)
For Each folderNode1 As XmlNode In folderEnumerable1
Dim folderId1 As String = ExtractId(folderNode1.Name)
Dim folderNode2 As XmlElement = xdoc2.CreateElement("Folder")
folderNode2.SetAttribute("Id", folderId1)
CopyAttributes(folderNode1, folderNode2, _
{"Name", "Property", "AlwaysCreate", "DefaultLocation"})
foldersNode2.AppendChild(folderNode2)
Dim filePattern As String = _
"DeployProject/Deployable/File/*[Folder _
[@value=""" & folderId1 & """]]"
Dim fileList1 As XmlNodeList = xdoc1.SelectNodes(filePattern)
Dim fileEnumerable1 As System.Linq.IOrderedEnumerable(Of XmlNode) =
fileList1.Cast(Of XmlNode)().OrderBy(Function(n) _
n.SelectSingleNode("SourcePath/@value").Value)
For Each fileNode1 As XmlNode In fileEnumerable1
Dim sourcePath1 As String = _
fileNode1.SelectSingleNode("SourcePath/@value").Value
Dim fileNode2 As XmlElement = xdoc2.CreateElement("File")
CopyAttributes(fileNode1, fileNode2, _
{"SourcePath", "Exclude", "IsDependency"})
folderNode2.AppendChild(fileNode2)
Next
ConvertFolderList(folderNode1, folderNode2)
Next
End If
End Sub
ConvertXmlVDProj
This method converts an XML file to vdproj with a 1:1 mapping. It is the translation to VB.NET of the code in VDProjectXML on GitHub.
Prerequisites
This project needs Visual Studio 2010. Later versions do not support setup projects.
Compiling and Launching
- In Visual Studio, open the project VDProjXml\VDProjXml.vbproj.
- Right-click on the project and click on "Build".
- Verify that WinDiff exists in the location "C:\Program Files\Microsoft SDKs\Windows\v7.0A\bin\WinDiff.Exe". If WinDiff exists in another location, change the path in CompareVDProjSetups.bat and CompareXmlSetups.bat.
- Double-click on Demo\CompareVDProjSetups.bat. This compares the two versions of the setup project Setup1v1/Setup1.vdproj and Setup1v2/Setup1.vdproj. You will see that it is very difficult to find out what the difference is between the two versions.
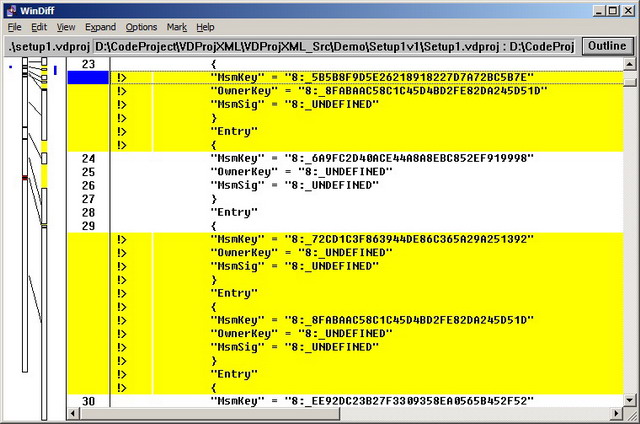
- Double-click on Demo\CompareXmlSetups.bat. This will convert the vdproj files in
Setup1v1 and Setup1v2 to XML files, and will compare the generated files Setup1v1\Setup1.p.xml and Setup1v2\Setup1.p.xml. You will see that the differences are only the two additional files and the version number.

- To convince yourself that the setup project files are correct:
- In Visual Studio, open the solution Demo\Demo.sln.
- Right-click on the solution and click on "Build Solution".
- In Visual Studio, open the solution Demo\Setup1v1\Setup1.sln.
- Right-click on the solution and click on "Build".
- In Visual Studio, open the project Demo\Setup1v2\Setup1.sln.
- Right-click on the solution and click on "Build".
- Double-click on Demo\Setup1v1\Release\Setup1.exe
- This will install
Setup1 version 1. - Double-click on C:\Program Files\Manufacturer1\Setup1\ConsoleApplication1.exe.
- This will open a console window with the following text:
ConsoleApplication1 Hello
Before ClassLibrary1.Class1.Sub1
After ClassLibrary1.Class1.Sub1
Press any key to exit
- Double-click on Demo\Setup1v1\Release\Setup1.exe, and choose Remove.
- Double-click on Demo\Setup1v2\Release\Setup1.exe.
- This will install
Setup1 version 2. - Double-click on C:\Program Files\Manufacturer1\Setup1\ConsoleApplication2.exe.
- This will open a console window with the following text:
ConsoleApplication2 Hello
Before ClassLibrary2.Class1.Sub1
After ClassLibrary2.Class1.Sub1
Press any key to exit
- Double-click on Demo\Setup1v2\Release\Setup1.exe, and choose Remove.
Conclusion
Whenever changes are made to a .vdproj file, one may run the tool VDProjXML to generate the corresponding .p.xml file. Both files (.vdproj and .p.xml) are checked-in. The next time changes are made to the .vdproj file, a new .p.xml file may be generated with the VDProjXML tool. Comparing the old and new .p.xml files is much easier than comparing the old and new .vdproj files. This uncovers the errors done by the weird behaviour of Visual Studio.
History
- Converting .vdproj to .xml and vice versa. Converting .vdproj to .p.xml
