Introduction
This article introduces a dead simple HTML Sanitizer which you can use to clean up user-entered HTML or uploaded HTML documents.
Sanitized:
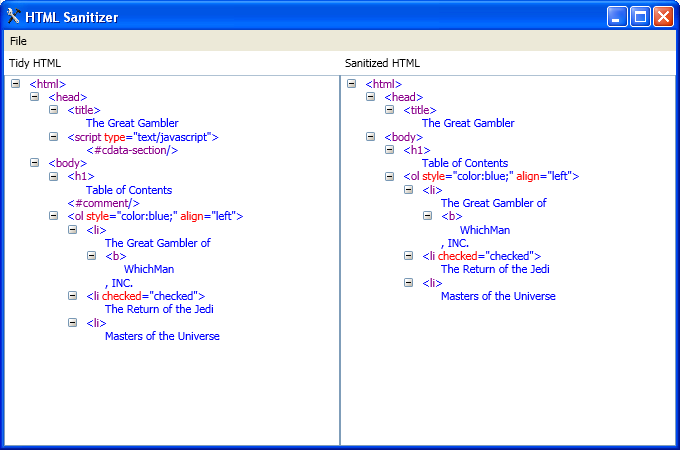
Original:

Background
One of our systems features a Document Production module which allows users to upload (and save) custom HTML documents which can be downloaded by other user. The problem was that some users kept adding "unsafe" script tags (and other XSS vulnerabilities) in their documents which we had to Sanitize.
Note: I know of the Microsoft Anti-Cross Site Scripting Library but decided to write my own since adding a new reference to the project was out of the question.
Using the code
const string input = "<scriPt>alert(0)</Script>This is the game <SCRIPT>";
var output = HtmlSanitizer.Sanitize(input);
Assert.AreEqual("This is the game ", output); Parse the HTML
You can also just parse the HTML document.
var input = System.IO.File.ReadAllText("myfile.htm");
var doc = HtmlParser.Parse(input);
Assert.AreEqual(2, doc.ChildNodes.Count);
Tidy the HTML
You can also just tidy the HTML content.
var input = "<input type=checkbox value=ON checked>";
var output = HtmlParser.Tidy(input);
Assert.AreEqual("<input type=\"checkbox\" value=\"ON\" checked=\"checked\"/>", output);
Points of Interest/References
- The XML Viewer used in this article was taken from A Simple XML Document Viewer Control
- This code has not been tested against extremely malformed HTML so please be careful how you use it.
- You can always change the list of unsafe tags and attributes to meet your requirements
History
This is the first revision of the article.
