Introduction
CLR (Common language runtime) is nothing new now, .NET developers are familiar with the CLR, how to work with the object. There is no doubt that now we can design our component and application easily using CLR.
We will not discuss about the CLR. We will try to focus on the DLR ((Dynamic Language Runtime). At first, we need to know what is DLR. In a simply world, we can say that the DLR has some new features which added to common language runtime (CLR) for Microsoft .NET Framework 4.0.
More information about CLR can be found here.
What Dynamic Types Do
Let’s try to get some more. One of the powerful features of Microsoft .NET Framework 4.0 is the Dynamic Types.
Dynamic Types allow us to write code in such a way that we can go around compile time checking. Note that bypass does not mean that we can remove the compile time errors, it means if the operation is not valid, then we cannot detect the error at compile time. This error will appear only in run time.
How to Work with Dynamic Types
Microsoft .NET Framework 4.0 provides us the System.Dynamic namespace. To use Dynamic Types, we need to add the references DLL of System.Dynamic.
Figure: Showing the dynamic type of current object output.
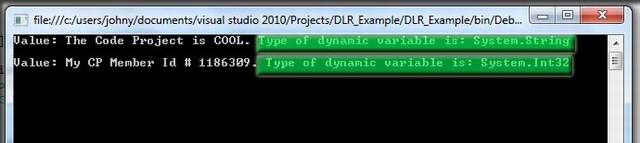
Well , I hope that you get the basics of DLR ((Dynamic Language Runtime), so let's try to play with a few code snippets and a few keywords of Microsoft Visual Studio .NET. We are familiar with the keyword “var” we will play with this keyword, before that one interesting thing I must share is that it is possible to change an object type runtime? Probably your answer will be NO. But objects defined with dynamic keyword can change their type at runtime. Isn't it cool. A simple code example is given below:
More information about System.Dynamic can be found here.
Using the Code
Here in this example below, we have a class called Class1(). The Class1() has two functions displayMessage() and displayNumeric(). Both functions are returning different values.
static void Main(string[] args)
{
dynamic myDynamicVariable;
var _objClass = new Class1();
myDynamicVariable = _objClass.displayMessage();
Console.WriteLine("Value: " + myDynamicVariable + ".
Type of dynamic variable is: " + myDynamicVariable.GetType());
myDynamicVariable = _objClass.displayNumeric();
Console.WriteLine("\nValue: My CP Member Id # " + myDynamicVariable +
". Type of dynamic variable is: " + myDynamicVariable.GetType());
Console.ReadLine();
}
class Class1
{
private string sMessage = "The Code Project is COOL";
public string displayMessage()
{
return sMessage;
}
public int displayNumeric()
{
return 1186309;
}
}
If you look, we have declared a dynamic variable myDynamicVariable.
dynamic myDynamicVariable;
So we are assigning string value to it and printing it in console, value as well as its type. This is all about Dynamic type.
Conclusion
I hope this might be helpful to you. Enjoy!
History
- 4th October 2010: Initial post
