Introduction
While studying electronic engineering and computer science, I participated in a compiler workshop where we had to write our own programming language. To view and analyse the syntax tree for a given program, I wrote a custom drawn tree component those days. The original component was written in Java and I thought it might be useful to have it as a CTreeCtrl derivate. In contrast to some other custom drawn tree controls at CodeProject, this one does not have its own data structure for representing the tree. This means that you do not have to write different code for inserting the tree items when you want to switch from CTreeCtrl. Because this control inherits from CTreeCtrl, it is very easy to activate the stock-functionality which draws the tree in the traditional way.

Algorithm for Displaying the Vertical Tree
The drawing algorithm for the vertical tree is based on two rules. The first one ascertains that leaf elements always have the same space between each other. And the other rule points out that the parent node always has to be drawn in the middle of its child elements. If you adapt these two rules to every node in the tree recursively in a pre-order sequence, then you will get what this control does.

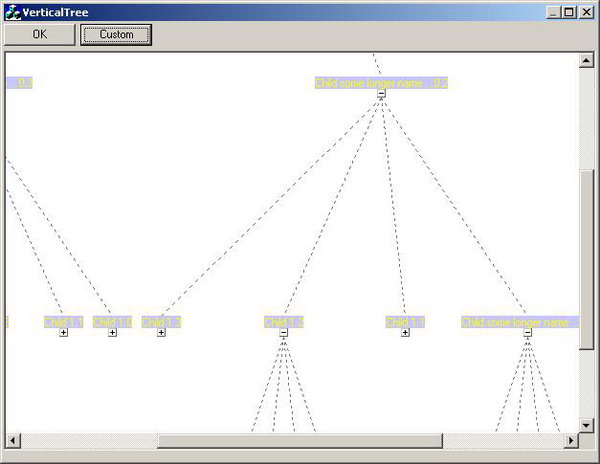
When the tree has to be drawn, the operation DrawItem(CDC *pDC, HTREEITEM item, int x, int level) is called for the root elements (refer to the illustration above / node 8). For the first item to draw, the starting x-position (see argument 3 of DrawItem) and the level are zero. As mentioned above, the algorithm iterates through all items recursively in a pre-order manner. So, if the current item has child elements, they are also expanded when it calls DrawItem for each of its children. However, if the current node is a leaf or if its children are collapsed, then DrawItem draws only the current item. The numbers in the boxes show the drawing sequence of the items. As you can see, the root node on which DrawItem was called first, is drawn last. Because of our second rule, this is not surprising.
After a tree node is drawn, DrawItem returns the x-position of the rightmost border of the item plus m_ItemSpaceX (refer to our first rule). For leaf items, the rightmost border is their own right border, while the rightmost border of the parent elements is the right border of the last child element.
Normally, I don't like to present too much source code in an article, but to analyse the algorithm, it might be useful for us.
int CVerticalTree::DrawItem(CDC *pDC, HTREEITEM item, int x, int level)
{
CString name = GetItemText(item);
CSize text_size = pDC->GetTextExtent(name);
int state = GetItemState(item, TVIF_STATE);
bool selected = (state & TVIS_SELECTED) != 0;
if (ItemHasChildren(item))
{
int left = x;
int right = 0;
int childcount = 0;
if (state & TVIS_EXPANDED)
for (HTREEITEM childitem = GetChildItem(item);
childitem != NULL;
childitem = GetNextItem(childitem, TVGN_NEXT))
{
right = DrawItem(pDC, childitem, x, level + 1);
x = right;
childcount++;
}
right = right - m_ItemSpaceX;
int width = right - left;
x = left + width / 2 - text_size.cx / 2;
if (x < left + m_ItemSpaceX)
x = left;
int y = level*m_ItemSpaceY;
DrawItemText(pDC, item, name,
x, level*m_ItemSpaceY,
text_size.cx, text_size.cy,
m_ItemBkColor, m_ItemTextColor);
if (m_bHasLines && (state & TVIS_EXPANDED))
{
int xstart = x + text_size.cx / 2;
int ystart = y + text_size.cy + BUTTON_SIZE;
CGdiObject *oldPen = pDC->SelectObject(&m_TreeLinePen);
for (HTREEITEM childitem = GetChildItem(item);
childitem != NULL;
childitem = GetNextItem(childitem, TVGN_NEXT))
{
ItemViewport *current = GetViewport(childitem);
pDC->MoveTo(xstart+m_OffsetX,ystart+m_OffsetY);
pDC->LineTo(current->x +m_OffsetX + current->cx / 2 ,
current->y + m_OffsetY);
}
pDC->SelectObject(oldPen);
}
if (m_bHasButtons)
{
pDC->Draw3dRect(x+m_OffsetX+text_size.cx / 2 - BUTTON_SIZE / 2,
y+m_OffsetY + text_size.cy, BUTTON_SIZE,
BUTTON_SIZE, RGB(200,200,200), RGB(100,100,100));
pDC->MoveTo(x+m_OffsetX+text_size.cx / 2 - BUTTON_SIZE / 2 + 2,
y+m_OffsetY + text_size.cy + BUTTON_SIZE / 2);
pDC->LineTo(x+m_OffsetX+text_size.cx / 2 + BUTTON_SIZE / 2 - 1,
y+m_OffsetY + text_size.cy + BUTTON_SIZE / 2);
if ((state & TVIS_EXPANDED) == 0)
{
pDC->MoveTo(x+m_OffsetX+text_size.cx / 2,
y+m_OffsetY + text_size.cy + 2);
pDC->LineTo(x+m_OffsetX+text_size.cx / 2,
y+m_OffsetY + text_size.cy + BUTTON_SIZE - 2);
}
}
if (right > x + text_size.cx)
return right + m_ItemSpaceX;
else
return x + text_size.cx + m_ItemSpaceX;
}
else
{
DrawItemText(pDC, item, name, x, level*m_ItemSpaceY,
text_size.cx, text_size.cy,
m_LeafBkColor, m_LeafTextColor);
return x + text_size.cx + m_ItemSpaceX;
}
}
Faults and Imperfections
The original Java control had some optimizations in the drawing routine which I could not adapt in this MFC version. If you take a look at the source code, you can recognize that the recursive calls to DrawItem won't stop even if items are not visible. Therefore, redrawing the control may be very expensive in some circumstances. Surprisingly, this control runs very fast with around 10000 elements. So, if you are not intending to handle an enormous amount of elements, then here you go. But you should keep this in mind if you want to use it in your applications.
License
This article has no explicit license attached to it, but may contain usage terms in the article text or the download files themselves. If in doubt, please contact the author via the discussion board below.
A list of licenses authors might use can be found here.
