Introduction
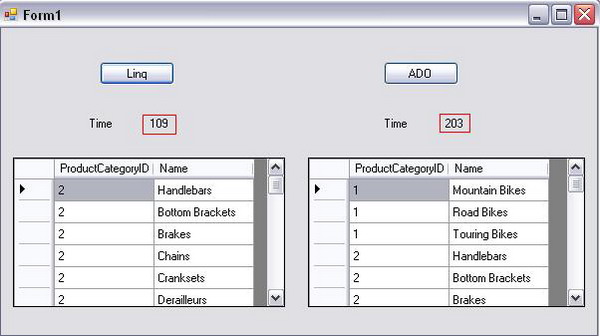
The article shows a simple comparison between LINQ to SQL and ADO.NET with regards to the execution time of selecting data from a SQL Server database. So, what is LINQ to SQL? LINQ to SQL provides a runtime infrastructure for managing relational data as objects without losing the ability to query. Your application is free to manipulate the objects while LINQ to SQL stays in the background tracking your changes automatically. LINQ to SQL gives you your database, tables, and columns as objects that you can use directly in your C# or VB.NET code. Here, we are going to test it with ADO.NET:
myDatabase.CustomersTable.CustomerNameColumn;
How to add LINQ
- LINQ is shipped with Microsoft Visual Studio 2008, you can download the beta for free from Microsoft.
- Open Visual Studio and create a new Windows Application project.
- Add New Item and choose LINQ to SQL classes.

- You will get a class .dbml that is inherited from
DataContext. - Now, from the Server Explorer, make a connection to the AdventureWorks database and then drag and drop the table Product in the designer.

- Move to the code..
Using the code
This application uses both ADO and LINQ, and calculates the time they take to select data from the AdventureWorks database. We are going to do something like select * from Products. In the LINQ button click event..
AdventureWorksDataContext AdventureDB = new AdventureWorksDataContext(
"Data Source=ISSY;Initial Catalog=AdventureWorks;Integrated Security=True");
var _data = from _products in AdventureDB.Products
select _products;
dataGridViewLinq.DataSource = _data;
In the ADO button click event:
SqlDataAdapter adapter = new SqlDataAdapter("select * from Production.Products",
"Data Source=ISSY;Initial Catalog=AdventureWorks;Integrated Security=True");
DataSet ds = new DataSet();
int x = adapter.Fill(ds);
dataGridViewADO.DataSource = ds.Tables[0];
Let's make it more complex; drag and drop the ProductCategroy table and the ProductSubCategory table in the DBML designer:

Using LINQ:
var _t = from o in AdventureDB.ProductSubcategories
where o.ProductCategory.ProductSubcategories.Count > 3
select new
{
o.ProductCategoryID,
o.Name,
};
dataGridViewLinq.DataSource = _t;
Using ADO.NET:
SqlDataAdapter adapter = new SqlDataAdapter("SELECT [t0].[ProductCategoryID],
[t0].[Name]"
+ "FROM [Production].[ProductSubcategory] AS [t0]"
+ "WHERE (("
+ "SELECT COUNT(*)"
+ "FROM [Production].[ProductCategory] AS [t1],
[Production].[ProductSubcategory] AS [t2]"
+ "WHERE ([t1].[ProductCategoryID] = [t0].[ProductCategoryID]) AND (
[t2].[ProductCategoryID] = [t1].[ProductCategoryID])"
+ ")) > 3",
"Data Source=ISSY;Initial Catalog=AdventureWorks;Integrated Security=True");
DataSet ds = new DataSet();
int x = adapter.Fill(ds);
dataGridViewADO.DataSource = ds.Tables[0];
The code:
private void buttonLinq_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
int startS = DateTime.Now.Second;
int startM = DateTime.Now.Millisecond;
AdventureWorksDataContext AdventureDB = new AdventureWorksDataContext(
"Data Source=ISSY;Initial Catalog=AdventureWorks;Integrated Security=True");
var _t = from o in AdventureDB.ProductSubcategories
where o.ProductCategory.ProductSubcategories.Count > 3
select new
{
o.ProductCategoryID,
o.Name,
};
dataGridViewLinq.DataSource = _t;
#region time_Calculation
int endS = DateTime.Now.Second;
int endM = DateTime.Now.Millisecond;
if (endS == startS)
{
labelLinqTime.Text = (endM - startM).ToString();
}
else if (endS > startS && endS < startS + 2)
{
labelLinqTime.Text = (endM + 1000 - startM).ToString();
}
else
{
throw new Exception("timeout");
}
#endregion
}
private void buttonADO_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
int startS = DateTime.Now.Second;
int startM = DateTime.Now.Millisecond;
SqlDataAdapter adapter = new SqlDataAdapter(
"SELECT [t0].[ProductCategoryID], [t0].[Name]"
+ "FROM [Production].[ProductSubcategory] AS [t0]"
+ "WHERE (("
+ "SELECT COUNT(*)"
+ "FROM [Production].[ProductCategory] AS [t1],
[Production].[ProductSubcategory] AS [t2]"
+ "WHERE ([t1].[ProductCategoryID] = [t0].[ProductCategoryID]) AND (
[t2].[ProductCategoryID] = [t1].[ProductCategoryID])"
+ ")) > 3",
"Data Source=ISSY;Initial Catalog=AdventureWorks;Integrated Security=True");
DataSet ds = new DataSet();
int x = adapter.Fill(ds);
dataGridViewADO.DataSource = ds.Tables[0];
#region time_calculation
int endS = DateTime.Now.Second;
int endM = DateTime.Now.Millisecond;
if (endS == startS)
{
labelADOTime.Text = (endM - startM).ToString();
}
else if (endS > startS && endS < startS + 2)
{
labelADOTime.Text = (endM + 1000 - startM).ToString();
}
else
{
throw new Exception("timeout");
}
#endregion
}
Change the query each time to avoid caching. Learn more about LINQ to SQL here.
