Introduction
SharePoint is a powerful application that enables an organization to quickly implement a web based portal for managing and sharing information among groups of people. Out of the box, it offers many components such as document libraries and configurable lists. For more advanced requirements, SharePoint provides the ability to create web parts, which are custom components that can plug into and interact with a SharePoint site. Web parts are a simple, yet powerful way to extend the capabilities of SharePoint to meet your organization’s unique requirements.
This article will show, step-by-step, how to create a simple SharePoint web part that implements a contact form. A contact form is typically used on a public website to provide a way for customers, business partners, and others outside the company to submit questions or request information by filling out fields on a web page and clicking a Submit button. This web part will collect the user’s name, email address, phone number, and message, and send the information to an email address when the user clicks Submit.
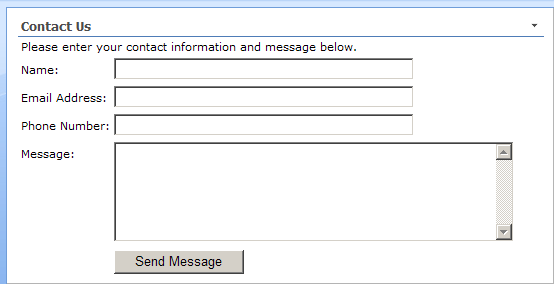
Requirements
The web part created in this article will use Windows SharePoint Services (WSS) 3.0. It will also work with MOSS 2007, which is a more advanced version of SharePoint built on the same infrastructure as WSS 3.0. To create the web part, we will be using Visual Studio 2008 installed on Windows Server 2003, along with Windows SharePoint Services 3.0 Tools: Visual Studio 2008 Extensions, Version 1.2, which is a free download from the Microsoft Download Center.
Creating a Web Part Project
The first step is to create a new web part project using Visual Studio 2008. To do this, open Visual Studio 2008, and choose New – Project from the file menu. Select Visual C# - SharePoint from the Project Type list, and select the Web Part template from the list on the right. Enter ContactFormWebPart as the name and the solution name, and choose a directory where you want the solution files to be saved. When you click OK, an empty web part project will be created and opened in Visual Studio.
The empty project has one web part, called WebPart1, but this isn’t what we want to call our web part, so the first step is to delete WebPart1 from the project by right clicking on the WebPart1 folder in the Solution Explorer in Visual Studio and choosing Delete.
Next, let's add a new web part to the project, called ContactForm. Right click on the ContactFormWebPart project in the Solution Explorer, and choose Add – New Item from the context menu. Select SharePoint from the categories list, and Web Part from the templates list. Enter ContactForm for the name, and click Add.

This gives you a new source file called ContactForm.cs that has an empty class inheriting from WebPart, with some TODO comments. In the next section, we are going to replace the CreateChildControls() function and add some additional code to this class.

Adding Code to Create the Controls
Now, we are ready to begin writing code that will display the web part. Open ContactForm.cs, and you will see a function called CreateChildControls(). This function is where we will add labels, textboxes, and a button to allow the user to interact with our web part.
But first, let's create some class-level variables for the controls that we will create. Declaring them at the class level as opposed to within the CreateChildControls() function will allow us to reference these controls from the button event handler later on.
TextBox txtContactName;
TextBox txtEmailAddress;
TextBox txtPhone;
TextBox txtMessage;
Button btnSendMessage;
Label lblMessageSent;
Now, let's add the code to CreateChildControls to build the display. In order to keep it simple, an HTML table will be used to align the controls in a consistent manner. Each table row will have two cells: one for the field label, and the other for the text boxes. Controls are created one at a time and added to a table cell, which is then added to a table row.
protected override void CreateChildControls()
{
base.CreateChildControls();
Table t;
TableRow tr;
TableCell tc;
t = new Table();
tr = new TableRow();
tc = new TableCell();
tc.ColumnSpan = 2;
tc.VerticalAlign = VerticalAlign.Top;
Label lblInstructions = new Label();
lblInstructions.Text = "Please enter your contact" +
" information and message below.";
tc.Controls.Add(lblInstructions);
tr.Controls.Add(tc);
t.Controls.Add(tr);
tr = new TableRow();
tc = new TableCell();
tc.Style["padding-top"] = "7px";
tc.VerticalAlign = VerticalAlign.Top;
Label lblContactName = new Label();
lblContactName.Text = "Name:";
tc.Controls.Add(lblContactName);
tr.Controls.Add(tc);
tc = new TableCell();
tc.VerticalAlign = VerticalAlign.Top;
txtContactName = new TextBox();
txtContactName.ID = "txtContactName";
txtContactName.Width = Unit.Pixel(300);
tc.Controls.Add(txtContactName);
tr.Controls.Add(tc);
t.Controls.Add(tr);
tr = new TableRow();
tc = new TableCell();
tc.Style["padding-top"] = "7px";
tc.VerticalAlign = VerticalAlign.Top;
Label lblEmailAddress = new Label();
lblEmailAddress.Text = "Email Address:";
tc.Controls.Add(lblEmailAddress);
tr.Controls.Add(tc);
tc = new TableCell();
tc.VerticalAlign = VerticalAlign.Top;
txtEmailAddress = new TextBox();
txtEmailAddress.ID = "txtEmailAddress";
txtEmailAddress.Width = Unit.Pixel(300);
tc.Controls.Add(txtEmailAddress);
tr.Controls.Add(tc);
t.Controls.Add(tr);
tr = new TableRow();
tc = new TableCell();
tc.Style["padding-top"] = "7px";
tc.VerticalAlign = VerticalAlign.Top;
Label lblPhone = new Label();
lblPhone.Text = "Phone Number:";
tc.Controls.Add(lblPhone);
tr.Controls.Add(tc);
tc = new TableCell();
tc.VerticalAlign = VerticalAlign.Top;
txtPhone = new TextBox();
txtPhone.ID = "txtPhone";
txtPhone.Width = Unit.Pixel(300);
tc.Controls.Add(txtPhone);
tr.Controls.Add(tc);
t.Controls.Add(tr);
tr = new TableRow();
tc = new TableCell();
tc.Style["padding-top"] = "7px";
tc.VerticalAlign = VerticalAlign.Top;
Label lblMessage = new Label();
lblMessage.Text = "Message:";
tc.Controls.Add(lblMessage);
tr.Controls.Add(tc);
tc = new TableCell();
tc.VerticalAlign = VerticalAlign.Top;
txtMessage = new TextBox();
txtMessage.ID = "txtMessage";
txtMessage.Height = Unit.Pixel(100);
txtMessage.Width = Unit.Pixel(400);
txtMessage.TextMode = TextBoxMode.MultiLine;
txtMessage.Wrap = true;
tc.Controls.Add(txtMessage);
tr.Controls.Add(tc);
t.Controls.Add(tr);
tr = new TableRow();
tc = new TableCell();
tr.Controls.Add(tc);
tc = new TableCell();
tc.VerticalAlign = VerticalAlign.Top;
lblMessageSent = new Label();
lblMessageSent.Text = "Your message has been sent. Thank you.";
lblMessageSent.Font.Bold = true;
lblMessageSent.Visible = false;
tc.Controls.Add(lblMessageSent);
tr.Controls.Add(tc);
t.Controls.Add(tr);
tr = new TableRow();
tc = new TableCell();
tr.Controls.Add(tc);
tc = new TableCell();
btnSendMessage = new Button();
btnSendMessage.Text = "Send Message";
btnSendMessage.Click += new EventHandler(btnSendMessage_Click);
tc.Controls.Add(btnSendMessage);
tr.Controls.Add(tc);
t.Controls.Add(tr);
this.Controls.Add(t);
}
Finally, we need to add an event handler to send the message as an email when the Send Message button is clicked by the user. In the code above, the event handler was already wired up with the line btnSendMessage.Click += new EventHandler btnSendMessage_Click);, so now we just need to create the btnSendMessage_Click function. This function simply builds an email message using text that was entered into the text boxes, and sends the email using SharePoint's SPUtility.SendEmail() function.
You will need to change the "to" and "from" fields in the message header for your specific situation. The "to" field specifies where the email will be sent, and the "from" field is the email address that the email should appear to be from. The "from" field isn't too important, but some mail servers may require this to be a valid email address.
protected void btnSendMessage_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
System.Text.StringBuilder subject = new System.Text.StringBuilder();
subject.Append("Contact Form Message from ");
subject.Append(txtContactName.Text);
System.Text.StringBuilder message = new System.Text.StringBuilder();
message.Append("Contact Name: ");
message.AppendLine(txtContactName.Text);
message.Append("Email Address: ");
message.AppendLine(txtEmailAddress.Text);
message.Append("Phone: ");
message.AppendLine(txtPhone.Text);
message.AppendLine();
message.AppendLine("Message:");
message.AppendLine(txtMessage.Text);
System.Collections.Specialized.StringDictionary messageHeader =
new System.Collections.Specialized.StringDictionary();
messageHeader.Add("to", "CustomerService@example.com");
messageHeader.Add("from", "ContactForm@example.com");
messageHeader.Add("subject", subject.ToString());
messageHeader.Add("content-type", "text/plain");
Microsoft.SharePoint.Utilities.SPUtility.SendEmail(
SPContext.Current.Web, messageHeader, message.ToString());
lblMessageSent.Visible = true;
txtContactName.Text = "";
txtEmailAddress.Text = "";
txtPhone.Text = "";
txtMessage.Text = "";
}
Testing the Web Part
Now, we are ready to test the web part. The easiest way to do this is to choose Deploy Solution from the Build menu in Visual Studio 2008. After it has built and deployed successfully, open a web browser and navigate to the SharePoint website. From the Site Actions menu, choose Edit Page. This will place the page into Edit Mode, where web parts can be added, removed, and configured.
For testing purposes, we don't care about the exact placement of the web part, so just click Add a Web Part in the main left zone. This will open up a dialog box listing all of the web parts that are available for use on this SharePoint server. If you scroll down the list, you should see the ContactForm web part. Put a checkbox next to this web part, and click the Add button.

You should now see the contact form displayed on the page. While still in Edit Mode, you can change other settings such as the title that is displayed above the web part, or the height and width. For testing, we are going to leave everything as the default, so just click the Exit Edit Mode button. The page will now show the contact form, and we are ready to test it. Enter a name, email address, phone number, and message, and click Send Message. If all is successful, you will see a message saying your message has been sent, and within a few minutes, receive the email that was generated by btnSendMessage_Click().

Checking the Outgoing E-Mail Settings
If your receive an error message when you click Send Message, or if the email does not arrive within 5 or 10 minutes, it could be that the outgoing email settings have not been configured in SharePoint. This can be done by a SharePoint administrator using the Central Administration website. In Central Administration, go to the Operations tab, and select Outgoing E-Mail Settings. Make sure the Outbound SMTP Server is configured with the name of the mail server.

Deploying the Web Part
Once you have tested the web part, it is ready to be deployed as a solution to the production SharePoint server. For this, we will create a SharePoint solution package, which is a .cab file that has a .wsp extension. The .wsp file is created automatically when you choose Deploy from within Visual Studio. Change the active configuration in Visual Studio from Debug to Release, and then choose Deploy Solution from the Build menu.
After it has successfully deployed the release version to your local SharePoint server, there will be a file called ContactFormWebPart.wsp in the /bin/Release subfolder of your project directory. Copy this file to a folder on your production SharePoint web server, or to a location that can be accessed from this server. Then, run the following commands from a command prompt on the production SharePoint web server. These commands will add the solution to SharePoint and then deploy the solution, making it available for use by all sites.
C:\>stsadm -o addsolution -filename ContactFormWebPart.wsp
C:\>stsadm -o deploysolution -name ContactFormWebPart.wsp -immediate
-allowgacdeployment -allcontenturls
Now, the web part is available for use on the production SharePoint server. Only one more thing is left to do. When you want to use it in a SharePoint site, you will need to add it to that site's web part gallery. To do this, navigate to your SharePoint site and go to Site Actions - Site Settings. Then, click on the Web Parts link under the Galleries section. This opens up a web page listing the web parts that are currently available for this site. Click New to add a new web part to the list. The next web page shows the deployed web parts. Check the box next to ContactFormWebPart.ContactForm, and then click the Populate Gallery button.
You should now see the Contact Form Web Part in the list of web parts in this site's gallery. Once the web part is in the gallery, you can edit a page in the site, and add the web part to the page, just as we did during testing.
Additional Improvements
There are some improvements that can be made to the Contact Form Web Part that we've created, but these are beyond the scope of this article. Here are some ideas for improving the Contact Form Web Part:
First, we could add validation to the fields to make sure that the required fields are filled in and that the data entered matches the expected format. For example, contact name should be required, message should be required, the email address should match the typical format of an email address, and the phone number should be in the format of a valid phone number.
Second, we could add properties to the web part to allow customization of the label text and the to and from addresses used for sending the email. These properties would allow changes to be made to the web part's appearance while editing the page in SharePoint, instead of requiring those changes to be made in the source code.
Additional Development Environment Options
Web parts can be created using Visual Studio 2005, but Visual Studio 2008 in conjunction with the downloadable extensions for WSS 3.0 make packaging and deploying your web part much easier. I highly recommend using Visual Studio 2008 for web part development, if possible.
In order to use the WSS extensions for Visual Studio 2008, the development environment needs to run on a SharePoint server. But, many developers use a client Operating System for their development instead of a server Operating System, which is required by SharePoint. This is where Microsoft Virtual PC can be really helpful. The Virtual PC will allow you to run another computer instance virtually, on your development PC, so you can create a Virtual PC image for your SharePoint web part development environment.
If you are new to web part development and want to try it out without the work of setting up a full SharePoint environment, Microsoft provides a Windows SharePoint Services 3.0 SP1 Developer Evaluation VPC Image that has WSS 3.0, Visual Studio, and the extensions already installed. You can use this with Virtual PC for an "instant" SharePoint environment.
Conclusion
In this article, you learned how to create a simple web part for SharePoint that implements a contact form that collects information and sends it as an email to a recipient. There are many more possibilities for the use of web parts, including communicating with other web parts in SharePoint, and integrating with external databases and applications. The ability of SharePoint to use custom web parts is a powerful feature that can be used to extend the functionality of SharePoint beyond what is possible with basic customization.
Revision History
- 12/08/2008 - Initial version.
