Introduction
Creating various web services, we can very easily also create client proxies for the PC in various ways: meaning of the tool Add service reference in Visual Studio or simply setting parameters in a command line svcutil.exe, receiving on exit a code and configuration file. But what do we do if the business concerns portable devices like Pocket PC or Smartphone? Fortunately, there is a solution to this problem which I am going to describe in given article.
Solution to the Problem
For example, we are going to create the new WCF web service in Visual Studio 2008 - File -> New -> Project -> Web -> WCF Service Application with name BooksService. Then, having created the necessary types of the data and function, we start our web service. It will be possibly in IIS 6.0/7.0 or built-in VS2008 ASP.NET Developer Server. Well, now it is possible to ask a fair question - how do we connect from the pocket computer to our service? Fortunately, instead of writing your own proxy class, there is a simpler way which consists of using the utility netcfsvcutil.exe, which you can download from this link. Then, let's set in parameters of the given utility in the next line: "http://192.168.134.10:8888/BooksService.svc". On exit, we will receive two files: CFClientBase.cs and BooksServie.cs. It is just what is necessary for us. Now I will, in detail, tell about the creation of service and the convenient mobile client for it.
WCF Service
After creation of this web service, we declare its interface as follows:
[ServiceContract]
public interface IBooksService
{
[OperationContract]
string[] GetBookNames();
[OperationContract]
Book[] GetBooks(GetBookType type, string input);
[OperationContract]
Book[] GetAllBooks();
}
As you can see, it is the Book class used in this piece of code. Its implementation looks as follows:
[DataContract]
public class Book
{
[DataMember]
public string Name { get; set; }
[DataMember]
public string Author { get; set; }
[DataMember]
public string ISBN { get; set; }
[DataMember]
public decimal Price { get; set; }
[DataMember]
public string Description { get; set; }
}
public enum GetBookType
{
ISBN, Name, Author
}
But when does the service takes this information about books? Not to complicate an example working with such databases as SqlServer or Oracle, we will store our data in an XML file data.xml which is built in folder App_Data.
<Books>
<Book>
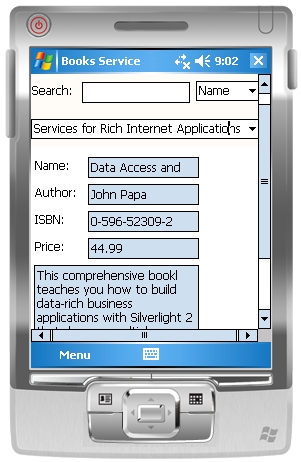
<Name>Data Access and Web Services for Rich Internet Applications</Name>
<Author>John Papa</Author>
<ISBN>0-596-52309-2</ISBN>
<Price>44,99</Price>
<Description>This comprehensive bookl teaches you how to build
data-rich business applications with Silverlight 2 that draw on
multiple sources of data. Packed with reusable examples,
Data-Driven Services with Silverlight 2 covers all of the data access
and web service tools you need, including data binding, the LINQ
data querying component, RESTful and SOAP web service support,
cross-domain web service calls, and Microsoft's new ADO.NET Data Services
and the ADO.NET Entity Framework.</Description>
</Book>
...
<Books>
The implementation of IBooksService interface is as follows:
public class BooksService : IBooksService
{
XDocument document = XDocument.Load(String.Format("{0}\\{1}\\{2}",
HostingEnvironment.ApplicationPhysicalPath, "App_Data",
"data.xml"));
public string[] GetBookNames()
{
var q = from dest in document.Root.Elements("Book")
select dest.Element("Name").Value;
return q.ToArray();
}
public Book[] GetBooks(GetBookType type, string input)
{
switch (type)
{
case GetBookType.ISBN:
{
var q = from dest in document.Root.Elements("Book")
where dest.Element("ISBN").Value ==
input
select new Book()
{
Author = dest.Element("Author").Value,
Description = dest.Element("Description").Value,
ISBN = dest.Element("ISBN").Value,
Name = dest.Element("Name").Value,
Price = Convert.ToDecimal(dest.Element("Price").Value)
};
return q.ToArray();
}
case GetBookType.Author:
{
var q = from dest in document.Root.Elements("Book")
where dest.Element("Author").Value.ToLower().
IndexOf(input.ToLower()) != -1
select new Book()
{
Author = dest.Element("Author").Value,
Description = dest.Element("Description").Value,
ISBN = dest.Element("ISBN").Value,
Name = dest.Element("Name").Value,
Price = Convert.ToDecimal(dest.Element("Price").Value)
};
return q.ToArray();
}
case GetBookType.Name:
{
var q = from dest in document.Root.Elements("Book")
where dest.Element("Name").Value.ToLower().
IndexOf(input.ToLower()) != -1
select new Book()
{
Author = dest.Element("Author").Value,
Description = dest.Element("Description").Value,
ISBN = dest.Element("ISBN").Value,
Name = dest.Element("Name").Value,
Price = Convert.ToDecimal(dest.Element("Price").Value)
};
return q.ToArray();
}
default:
{
return new List<book />().ToArray();
}
}
}
public Book[] GetAllBooks()
{
var q = from dest in document.Root.Elements("Book")
select new Book()
{
Author = dest.Element("Author").Value,
Description = dest.Element("Description").Value,
ISBN = dest.Element("ISBN").Value,
Name = dest.Element("Name").Value,
Price = Convert.ToDecimal(dest.Element("Price").Value)
};
return q.ToArray();
}
}
As you can see, I work with XML data using LINQ to XML because it is the easiest way for me. Now, when we have a ready service, we can place it on any hosting and be connected to the set address. So, we will start the most interesting part of work - the creation of the pocket client for it.
PDA Client
To begin with, you should create the new project Smart Device Project. After that, you will have a new pure form and automatically created code of initialization for it. On it, meanwhile it is possible to stop. As I said in "Solution to the Problem" section, you should run netcfsvcutil.exe and start with the necessary parameters for you. You should attach CFClientBase.cs and BooksService.cs files to your current project. You now have a ready proxy class for work. Let's look at how to correctly initialize the connection to our service:
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
try
{
string remoteAddress = HelpClass.BuildUrl();
EndpointAddress endpoint = new EndpointAddress(remoteAddress);
client = new BooksServiceClient(new BasicHttpBinding(),
endpoint);
comboBox1.Items.Clear();
foreach (string s in client.GetBookNames())
{
comboBox1.Items.Add(s);
}
books.Clear();
books.AddRange(client.GetAllBooks());
seed = 0;
if (books.Count > 1)
button1.Enabled = true;
comboBox1.SelectedIndex = 0;
}
catch (Exception ex) { MessageBox.Show(string.Format
("Connection Error: {0}", ex.Message)); }
}
The HelpClass class has been used:
public static class HelpClass
{
static XDocument doc = XDocument.Load
(Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().GetName().CodeBase.Substring(0,
Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().GetName().CodeBase.LastIndexOf('\\') + 1) +
"settings.xml");
public static string BuildUrl()
{
return string.Format("http:/ /a{0}:{1}/BooksService.svc",
doc.Root.Element("Host").Value, doc.Root.Element("Port").Value);
}
}
So, after the connection to a final point, you can high-grade use all functions which the web service provides.
Conclusion
All in all, as you can be convinced, the creation of the elementary client to service does not require special work. All basic work on proxy creation is incurred by the utility netcfsvcutil.exe, on your responsibility in instructions of the service address and initialization of the client through basicHttp binding. Good luck!

History
- 14th June, 2009: Initial post
