Introduction
System Requirements
- Windows XP, 7, Vista, 8, 8.1, 10, 11
- .NET Framework v4
About This Solution
- This solution contains two windows applications, one for serial port and the other for parallel port
- VB is used to develop a very simple RS232 Controller application that makes use of serial port easy.
- It supports storing your command in text file for later use
- It support file sending to serial port
- A separate application is made for parallel port controller
- This solution also contains a Most Recently Files menu strip library that used in RS232 controller to make track to last files used and this library could be used in any Windows application.
Using This Application
- Download and install the application
- Connect your device to the computer with the suitable cable
- Switch on your machine
- Run the application and use it to send and receive data for your machine
- Store your command or the machine output for later use
Reasons for Using Machine Controller
If you need to extend your machine usage, you may need to control it via Machine Controller. This can be in these categories: time based controlling, event, and communication.
Time Based Controlling
Time-based actions include actions based on a set amount of time passing, or in action in a specific time.
Event Based Controlling
If you want the machine to do something on a specific condition, or when something else has happened.
Communication Controlling
It will help in sending commands or data to the machine to change its start up or run status or receive data from the machine to be proceeded by another applications.
What is Serial Port
Serial port is a serial communication physical interface through which information transfers in or out one bit at a time (in contrast to a parallel port). Throughout most of the history of personal computers, data was transferred through serial ports to devices such as modems, terminals, and various peripherals.
What is RS-232
Recommended Standard-232 is a standard for serial transmission between computers and peripheral devices. Using a 25-pin DB-25 or 9-pin DB-9 connector, its normal cable limitation of 50 feet can be extended to several hundred feet with high-quality cable. Many equipment and machines have their built-in RS232 port. Making use of this port is very simple. All programming languages sport this port.
About Parallel Port
Parallel port, printer port, or LPT port is another easy way for communicating with external devices. I provide an application that can be used to control parallel port connecting devices. The direct port access in Windows NT versions is not allowed, so we need to have a driver in order to communicate with ports directly. Therefore, we are using a freeware driver and library. This library supports 32 bit and 64 bit versions of Windows for both x86 and x64 CPU.
Communicating with the Parallel Port
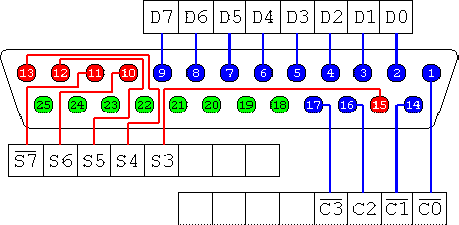
The parallel port usually comes as a 25-pin female port and it is commonly used to connect printers to a computer. It could be use to control relays box. Many companies provide a relays box for parallel port that could be used as PLC to controls machines. The parallel port contains three types of registers: data, status and control registers. status register is a read only register to get port status.
Points of Interest
About Most Recently Files Library
- We first build the
MostRecentlyFilesItem class that inherits ToolStripMenuItem - We add a property
FileName - Once you set the
FileName property, the text of this menu item will be changed to the number of the file and the file name
public sealed override string Text
{
get
{
try
{
if (this.Enabled)
{
var number = this.Index + 1;
var sEntryName = ShortenPathname(this.FileName);
if (number < 10)
{
return "&" + number + " " + sEntryName;
}
else if (number == 10)
{
return "1&0" + " " + sEntryName;
}
else
{
return number + " " + sEntryName;
}
}
else
{
return DefaultText;
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
if (_ErrMsg.ErrMsg(ex))
{
System.Diagnostics.Debugger.Break();
}
return null;
}
}
set
{
}
}
Public NotOverridable Overrides Property Text As String
Get
Try
If Me.Enabled Then
Dim number = Me.Index + 1
Dim sEntryName = ShortenPathname(Me.FileName)
If number < 10 Then
Return "&" & number & " " & sEntryName
ElseIf number = 10 Then
Return "1&0" & " " & sEntryName
Else
Return number & " " & sEntryName
End If
Else
Return DefaultText
End If
Catch ex As Exception
If ErrMsg(ex) Then Diagnostics.Debugger.Break()
Return Nothing
End Try
End Get
Set(value As String)
End Set
End Property
Then we build the main menu item manger that will control the menu items:
public class MostRecentlyFiles : MostRecentlyFilesItem, IList<string>
Public Class MostRecentlyFiles
Inherits MostRecentlyFilesItem
Implements IList(Of String)
- The previous class is inherited to act as one of the file menu items and makes the control of it form the denser
- It is
Implements IList(Of String) to act as a list of files, just add file to it and it will be viewed correctly in the menu items - To set all items, you could call the
IList.AddRange method Files property is added to get or set a comma separated list of files in the menu- If any file does not exist, it will be ignored.
public void Add(string sFileName)
{
try
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(sFileName) || !System.IO.File.Exists(sFileName))
{
return;
}
this.Enabled = true;
if (Count > 0)
{
int Index = _EntriesFiles.IndexOf(sFileName);
if (Index >= 0)
{
if (Index == 0)
{
return;
}
this._EntriesFiles.Remove(sFileName);
this._EntriesFiles.Insert(0, sFileName);
for (int i = 0; i < this._EntriesFiles.Count; i++)
{
this._EntriesItems[i].FileName = this._EntriesFiles[i];
}
return;
}
}
while (!(this.Count <= _EntriesMaxCount))
{
this.RemoveAt(this.Count - 1);
}
MostRecentlyFilesItem menuItem = null;
if (this.Count == 0 && !HasDropDownItems)
{
this.Initialize(this, sFileName, OnClick);
menuItem = this;
}
else
{
menuItem = new MostRecentlyFilesItem(this, sFileName, OnClick);
MenuItems.Insert(StartIndex, menuItem);
}
this._EntriesFiles.Insert(0, sFileName);
this._EntriesItems.Insert(0, menuItem);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
if (_ErrMsg.ErrMsg(ex))
{
System.Diagnostics.Debugger.Break();
}
}
}
Public Sub Add(ByVal sFileName As String) Implements IList(Of String).Add
Try
If String.IsNullOrEmpty(sFileName) OrElse Not IO.File.Exists(sFileName) Then
Exit Sub
End If
Me.Enabled = True
If Count > 0 Then
Dim Index As Integer = _EntriesFiles.IndexOf(sFileName)
If Index >= 0 Then
If Index = 0 Then Exit Sub
Me._EntriesFiles.Remove(sFileName)
Me._EntriesFiles.Insert(0, sFileName)
For i As Integer = 0 To Me._EntriesFiles.Count - 1
Me._EntriesItems(i).FileName = Me._EntriesFiles(i)
Next
Exit Sub
End If
End If
Do Until Me.Count <= _EntriesMaxCount
Me.RemoveAt(Me.Count - 1)
Loop
Dim menuItem As MostRecentlyFilesItem
If Me.Count = 0 AndAlso Not HasDropDownItems Then
Me.Initialize(Me, sFileName, AddressOf OnClick)
menuItem = Me
Else
menuItem = New MostRecentlyFilesItem(Me, sFileName, AddressOf OnClick)
MenuItems.Insert(StartIndex, menuItem)
End If
Me._EntriesFiles.Insert(0, sFileName)
Me._EntriesItems.Insert(0, menuItem)
Catch ex As Exception
If ErrMsg(ex) Then Diagnostics.Debugger.Break()
End Try
End Sub
Public Property Files As String
Get
If Count = 0 Then
Return ""
Else
Return Join(_EntriesFiles.ToArray, ",")
End If
End Get
Set(value As String)
Try
Me.Clear()
If String.IsNullOrEmpty(value) Then Exit Property
Dim vItems = Split(value, ",")
If vItems Is Nothing OrElse vItems.Length = 0 Then Exit Property
AddRange(vItems)
Catch ex As Exception
If ErrMsg(ex) Then Diagnostics.Debugger.Break()
End Try
End Set
End Property
About RS232Controller
- The built-in SerialPort control is extended to make writing and reading data more easy
DataReceived is monitored and when any new data is found, a DataReaded event is fired
public class SerialPortEx : SerialPort
{
public void OnDataReceived(object sender, SerialDataReceivedEventArgs e)
{
try
{
byte[] BytesReaded = new byte[this.BytesToRead];
int BytesReadedCount = this.Read(BytesReaded, 0, this.BytesToRead);
if (BytesReadedCount == 0)
{
return;
}
string sData = this.Encoding.GetString(BytesReaded, 0, BytesReadedCount);
OnDataReaded(sData, false);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
if (_ErrMsg.ErrMsg(ex))
{
System.Diagnostics.Debugger.Break();
}
}
}
public event EventHandler<LinkClickedEventArgs> DataReaded;
Public Class SerialPortEx
Inherits SerialPort
Public Sub OnDataReceived(sender As Object, e As SerialDataReceivedEventArgs) _
Handles Me.DataReceived
Try
Dim BytesReaded(Me.BytesToRead - 1) As Byte
Dim BytesReadedCount As Integer = Me.Read(BytesReaded, 0, Me.BytesToRead)
If BytesReadedCount = 0 Then
Exit Sub
End If
Dim sData As String = Me.Encoding.GetString(BytesReaded, 0, BytesReadedCount)
OnDataReaded(sData, False)
Catch ex As Exception
If ErrMsg(ex) Then Diagnostics.Debugger.Break()
End Try
End Sub
Public Event DataReaded As EventHandler(Of LinkClickedEventArgs)
About LPTController
- Several drivers are supported to read and write data.
- The application will check for the available driver to use.
- If no driver is found or no parallel port is found, a virtual driver is used.
PortIO class is the main class to read and write to ports and it could be used as follows:
PortIO vProtIO = new PortIO();
var Value = vProtIO.PortData;
var DataRegister0 = vProtIO.DataRegister(PortIO.BitRegister.Bit0);
vProtIO.PortData = Value;
vProtIO.SetDataRegister(PortIO.BitRegister.Bit0, DataRegister0);
Dim vProtIO As New PortIO
Dim Value = vProtIO.PortData
Dim DataRegister0 = vProtIO.DataRegister(PortIO.BitRegister.Bit0)
vProtIO.PortData = Value
vProtIO.SetDataRegister(PortIO.BitRegister.Bit0, DataRegister0)
PortIO Class Members
I use one class to access different libraries and this class has the following members:
Properties
Port: Sets or get the port to read and write toPortAddress: Gets the address of the selected portPortData: Gets or sets the value of all data registers in one byte valuePortControl: Gets or sets the value of all control registers in one byte valuePortStatus: Gets the value of all status registers in one byte valueIsTestSigning: Checks if the test signing for the drives is switching on or off
Functions and Methods
PortsCount: Gets the count of the available parallel ports in the PCInp: Gets the value of all registers in one byte value from a specific port addressOut: Sets the value of all registers in one byte value for a specific port addressInpPhys: Gets a value from physical memory (not supported by winring0)DataRegister: Gets the Boolean value of a specific data registerSetDataRegister: Sets the Boolean value of a specific data registerStatusRegister: Gets the Boolean value of a specific status registerControlRegister: Gets the Boolean value of a specific control registerSetControlRegister: Sets the Boolean value of a specific control registerIsAdmin: Checks if the application is run as administratorRunAsAdmin: Runs specific application as administratorRunAsAdminRestart: Restarts the current application as administrator
Events
GotError: Occurs when an error is raised in dealing with the library
Addressing the Parallel Port and Registers
Port addressing controls a great deal in port programming, as it is the door that enables programs to connect to the external circuit or device. Therefore, I would like to explain all the available port addresses.
In normal PCs, a parallel port address can vary depending on the BIOS settings and some other issues. The most common address is &h378, however you can get all parallel port addresses from the BIOS by checking the data stored in &H408 and the following function will do this: This function is a built-in PortIO class:
private void GetParallelPortAddress()
{
try
{
_PortsAddresses = new List<UInt16>();
for (int nPortNo = 0; nPortNo <= 9; nPortNo++)
{
var pPortAddressLocation = new IntPtr(0x408 + 2 * nPortNo);
var nPortAddress = _PortIO.InpPhys(pPortAddressLocation).ToInt32();
if (nPortAddress > 0 && nPortAddress < 0xFFF)
{
_PortsAddresses.Add(Convert.ToUInt16(nPortAddress));
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_ErrMsg.ErrMsg(ex);
}
}
Private Sub GetParallelPortAddress()
Try
_PortsAddresses = New List(Of UInt16)
For nPortNo As Integer = 0 To 9
Dim pPortAddressLocation = New IntPtr(&H408 + 2 * nPortNo)
Dim nPortAddress = _PortIO.InpPhys(pPortAddressLocation).ToInt32
If nPortAddress > 0 AndAlso nPortAddress < &HFFF Then
_PortsAddresses.Add(CType(nPortAddress, UInt16))
Else
Exit For
End If
Next
Catch ex As Exception
ErrMsg(ex)
End Try
End Sub
Device Needed to Use LPT Controller
To use this application, you should get a Parallel Port Relay Box such as KIT 74 V2, CK1601, quasar.
To build a relay box yourself, remember that you could not drain much current for the bin as this would burn your parallel port or your entire motherboard. So use them at your own risk...!
Useful Links
