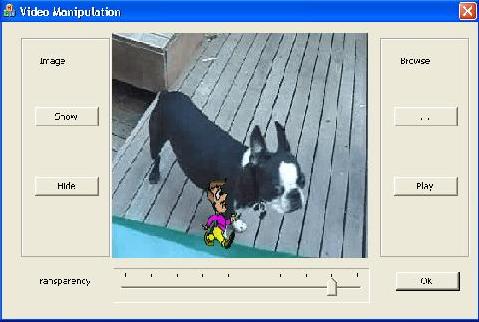
Introduction
Displaying anything over playing video does not seem like an easy task. Here in this article, I tried to display a picture over running video. Not a static image, but now in this updated article, it animates that image.
Updates
I updated my cVideo class to show an image animating. Not only this, but now you can control this image's transparency level also. See "Peeking Inside DirectShow" below.
Background
Displaying a picture over video requires some insight of DirectShow and how to build a filter graph. And, adding custom filters in the graph like VMR9 (video mixing renderer). This VMR9 is the key, it is the renderer which allows us to display a picture over video.
Building Environment
All applications which want to use DirectShow must include the header Dshow.h, and use the library Strmiids.lib.
Peeking Inside DirectShow
The basic force behind displaying an image over a video is the interface IVMRMixerBitmap9. Basically, this interface only has three member functions.
GetAlphaBitmapParameters()
SetAlphaBitmap()
UpdateAlphaBitmapParameters()
The other basic thing is a structure VMR9AlphaBitmap. This is basically used to convey data among functions. Some of the members of VMR9AlphaBitmap which are discussed here are given below:
DWORD dwFlags;
HDC hdc;
RECT rSrc;
VMR9NormalizedRect rDest;
FLOAT fAlpha;
COLORREF clrSrcKey;
Now comes the point of how to work with them. Let us see how to initialize the thing for the first time. First of all, we need to know:
- the handle to the device context
hDC in which we have selected (SelectObject) the image,
- the other important thing is the dimensions of the image,
- and the third thing which is required is where to show the image on the video (a rect),
- a transparency level, which tells how much transparent the image will be on the video.
- a colorkey if you want to hide the background color of the image; set it to the color of the background; it is not a must to hide only the background, you can give any color value, and the given color will be painted as transparent on the video,
- and at last, the set flags of the value which we have filled.
Now every thing is OK, just call SetAlphaBitmap().
For more insights, see my blog.
Basic Initialization
First of all, we need to create an object of the filter graph manager (the filter graph manager is used to control the filters and the data flow). This process is done by calling CoCreateInstance(). This way, we create an object of the filter graph manager and also get a pointer to the IGraphBuilder interface. This interface is then used for building a custom filter graph (the filter graph is the full set of DirectShow filters to play a media file).
CoCreateInstance(CLSID_FilterGraph, NULL, CLSCTX_INPROC_SERVER,
IID_IGraphBuilder, (void **)&pGraph);
After creating the filter graph manager, the other important issue is the addition of VMR9 in the filter graph. But before addition, we need to create it, and after creation, we will add that filter (VMR9) to our filter graph.
CoCreateInstance(CLSID_VideoMixingRenderer9, NULL, CLSCTX_INPROC,
IID_IBaseFilter, (void**)&pVmr);
pGraph->AddFilter(pVmr, L"Video");
Now we need to configure the VMR9 to our custom needs. Such as here, we are setting it to show the video in our provided window, setting the video position.
pVmr->QueryInterface(IID_IVMRFilterConfig9, (void**)&pConfig);
pConfig->SetRenderingMode(VMR9Mode_Windowless);
pVmr->QueryInterface(IID_IVMRWindowlessControl9, (void**)&pWC);
pWC->SetVideoPosition(NULL, pRect);
pWC->SetVideoClippingWindow(pParentWnd->m_hWnd);
The following IVMRMixerBitmap9 is the interface which provides us the facility to show an image over a video. And bmpInfo is a structure which holds the data about our image which we want to show over the video. Here for the first time, we are initializing it to have all zeros.
pWC->QueryInterface(IID_IVMRMixerBitmap9, (LPVOID *)&pBmp);
ZeroMemory(&bmpInfo, sizeof(bmpInfo) );
The following are the interfaces which are very necessary in any DirectShow application, because they provide the facility to control the data flow with IMediaControl, and notifies our application about any important event that occurs. For example, the file end reached, the interface which provides this facility is IMediaEventEx. With this interface, we need to set the window which we want to be notified. And another important interface is IMediaSeeking which provides the facility of seeking in the media file.
pGraph->QueryInterface(IID_IMediaControl, (void **)&pMC);
pGraph->QueryInterface(IID_IMediaEventEx, (void **)&pME);
pME->SetNotifyWindow ( ( OAHWND ) pParentWnd->GetParent()->m_hWnd,
WM_GRAPHNOTIFY, 0 ) ;
pGraph->QueryInterface(IID_IMediaSeeking, (void **)&pMS);
Now create the custom filter graph. And then run it. After this, the video will start playing in our given window.
pGraph->RenderFile(mFileToPlay, NULL);
pMC->Run();
Displaying the Image
The things we need to know are handle to the device context in which the image is selected, image size, the color value of the background of the image if you want to make the background (of the image) transparent (known as colorkey). Let us start now. First, get the device context of the window on which to play the video. Now we need another device context, which must be compatible with the video window device context, and now select the desired image in that device context.
CDC * pdc = GetDC();
CDC mCompatibleDC;
mCompatibleDC.CreateCompatibleDC(pdc);
mCompatibleDC.SelectObject(hBitmap);
CRect reSrc(0,0,mBitmapWidth,mBitmapHeight);
Now the actual work of displaying the image starts. Initialize the bmpInfo structure with the desired values, e.g., set the flags. Set the device context and the source rectangle, which is the image size.
bmpInfo.dwFlags |= VMRBITMAP_HDC;
bmpInfo.hdc = pDC->m_hDC;
bmpInfo.rSrc = rectSize;
Set the destination rectangle, which is the portion on the screen where to show the image.
bmpInfo.rDest.right = 1.0f;
bmpInfo.rDest.left = 1.0f - 0.3;
bmpInfo.rDest.top =1.0 - 0.3;
bmpInfo.rDest.bottom = 1.0f;
Set the transparency level.
bmpInfo.fAlpha = 0.0;
Set the colorkey value and its flag. Here it is set as Green color. It means any green color on the image will be treated as transparent.
bmpInfo.dwFlags |= VMRBITMAP_SRCCOLORKEY;
bmpInfo.clrSrcKey = RGB(0, 255, 0);
pBmp->SetAlphaBitmap(&bmpInfo);
Using the Code
I tried to keep things as simple as possible. I built a class cVideo. It is this class which hides all complexities from you. You just call this class's methods, and every thing else is handled by this class.
This class has following methods:
void InitInterfaces(BSTR mFileToPlay, CWnd* pParentWnd, CRect* pRect);
void Clean(void);
void Play(void);
void ShowImage(CDC* pDC, CRect rectSize);
void HideImage(void);
void SetTransparency( int tansparencyLevel )
void Animate();
InitInterfaces() hides all the mysteries of DirectShow graph building.
play(), as the name suggests, plays a file.
ShowImage() just provides the device context's pointer (CDC* pDC) in which you have selected the picture to be shown.
HideImage() just hides the shown image.
SetTransparency(int transparencyLevel) controls the transparency level of the image over the video.
Animate() updates the image showing the rectangle, simulating animation.
- at last,
Clean() releases the DirectShow interfaces.
History
- Updated 16 Sep 2006 - Now it describes every thing clearly.
- Updated 15 Sep 2006 - Added animated image and transparency control.
- 09 Sep 2006 - First version.
