Contents
Introduction
This article shows how to create a small application that sits on the task bar and provides the ability to copy preformatted text or code blocks to the clipboard, which may then be pasted into a program, document or web page as appropriate.
I first created this application when I found that I was repeatedly pasting the same comments or suggestions into CodeProject answers, in both Q&A and the Forums. I also used it as a learning (and I hope teaching) sample for a few features that can be used in many places when developing Win32 programs. For those who prefer to use MFC, a port of these ideas should be a fairly simple process; an exercise for the reader.
Note: This project has been developed under Windows 7 and Visual C++ Express 2010. For a version that works for Windows XP, see the section titled Windows XP version. The program is broken down into separate areas to try and show how each part may be used independently of the overall project. Some of the ideas have been taken from other CodeProject articles*, MSDN, and, of course, the wonderful Google.
*I have unfortunately not kept a record of all the articles I have referred to so apologies to those authors, but if you see anything here that may have originated in one of your articles, then let me know and I'll add an acknowledgement.
The program files used to build the project are:
- Header files
- Snippets.h: Local project and resource definitions
- StdAfx.h: The include headers used throughout the project
- Resource files
- Snippets.ico: Icon for the notification area
- Snippets.rc: Resource script - menu, dialogs, strings, version, etc.
- Source files
- DataReader.cpp: Code to read
strings from various sources and save in a vector - NotifyIcon.cpp: Code to setup the notification icon and respond to commands
- Snippets.cpp: Main portion of the Windows application, and message handler
- StdAfx.cpp: Used to generate the precompiled headers
Creating a Task bar Notification Application
The basis of this application is the taskbar notification icon, which allows an application to be accessed from a small icon that is placed in the taskbar notification area of the Windows desktop. The application itself is a 'normal' Windows application whose main window is generally not displayed by default (or in some cases ever). However, the application needs to create a main window in order to receive messages from the Windows operating system to take whatever actions are requested by the user.
The application is a simple Win32 Windows application, which follows the standard pattern of:
- Define and register a Windows class and its
WndProc message handler - Create a main window of this class and (possibly) display it on the screen - but not in our case
- Start the message pump to dispatch user messages to the application
- Handle messages and commands as and when they are received
The extra code needed for the notification icon is invoked just before starting the message loop and comprises the section below which adds our icon to the notification area of the taskbar.
static const GUID SnippetIconGUID =
{
0xe87633eb, 0xaf17, 0x47e4, 0xa4, 0x3c, 0xaf, 0xbd, 0x86, 0xe1, 0x76, 0xd5
};
static NOTIFYICONDATA notifyIconData;
BOOL NotifyInit(HWND hWnd,
HINSTANCE hInstance
)
{
pvContents = ReadData(MAKEINTRESOURCE(IDS_REGKEY), EX_REGVALUE); if (pvContents != NULL &&
pvContents->size() > 0)
{
SetLastError(-1);
return FALSE; }
notifyIconData.cbSize = sizeof notifyIconData; notifyIconData.hWnd = hWnd; notifyIconData.uID = IDR_MAINFRAME; notifyIconData.uFlags = NIF_MESSAGE | NIF_ICON | NIF_TIP | NIF_INFO | NIF_GUID | NIF_SHOWTIP; notifyIconData.uCallbackMessage = WM_USER_SHELLICON; notifyIconData.hIcon = LoadIcon(hInstance,
MAKEINTRESOURCE(IDR_MAINFRAME)); LoadString(hInstance, IDS_TOOLTIP, notifyIconData.szTip,
_countof(notifyIconData.szTip)); notifyIconData.dwState = 0; notifyIconData.dwStateMask = 0; LoadString(hInstance, IDS_BALLOONINFO, notifyIconData.szInfo,
_countof(notifyIconData.szInfo)); notifyIconData.uVersion = NOTIFYICON_VERSION_4; LoadString(hInstance, IDS_BALLOONTITLE, notifyIconData.szInfoTitle,
_countof(notifyIconData.szInfoTitle)); notifyIconData.dwInfoFlags = NIIF_USER; #if (_WIN32_WINNT >= 0x0600) // if Windows Vista or later
notifyIconData.guidItem = SnippetIconGUID; notifyIconData.hBalloonIcon = NULL;
#endif
return Shell_NotifyIcon(NIM_ADD, ¬ifyIconData);
}
Items of note in the above:
- The value stored in the
uCallbackMessage field is used by Windows to notify the application that the icon has been activated by the user (either by mouse or keyboard). This value should be greater than the value of WM_USER and unique within the application. - The
uVersion field should be adjusted for versions of Windows prior to Vista. - The GUID for the
guidItem should be generated by guidgen or similar. - The size of the tooltip and balloon information fields are as defined for the
NOTIFYICONDATA structure. - The
Shell_NotifyIcon() function adds the icon to the notification area and displays the balloon information for a few seconds. - The
ReadData() function returns a pointer to a vector which contains a number of pair objects, each containing a pair of strings: a title and a value, which are used to create the menu as described below.
The actual data used for snippet identifiers and their associated content is stored in a list that may be created from a number of different sources. The commonest method would be to have a table of strings within one of the source modules of the application or the resource script, but this means rebuilding the application whenever the list needs to be changed. Two possible alternatives are described in the following sections.
One of the common methods of storing configuration data for an application is to put it into the Registry under a key created for the application in question. Although this method is often frowned upon these days, it is still worth discussing as an exercise in learning how to make use of this Windows feature.
For the purposes of this program, I first created a Registry data file containing the information that I want, which will be saved under the key:
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\
Software\
CodeProject\
Snippets
The actual data will be stored as values, whose names are the strings that will appear on the context menu of the application, and whose values will be copied to the clipboard when a menu item is selected. This data may be manually loaded into the Registry, but it is far simpler to create a .reg file which can be easily edited with Notepad or any other text editor. These keys are then added to the Registry by double-clicking the .reg file or using the reg IMPORT or regedit /s command.
The content of the .reg file will look something like this where each entry comprises two quoted strings, the first becomes the name of the item and the second its value:
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\CodeProject\Snippets]
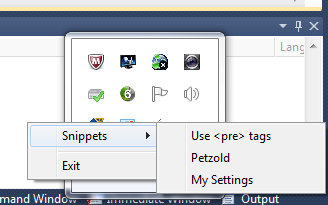
"Use <pre> tags"="Use the <span style=\"background-color:#FBEDBB;\">
code block</span> button, or add <pre></pre> tags"
"Petzold"="<a href=\"http://www.charlespetzold.com/dotnet/\">.NET Book Zero</a>
[<a href=\"http://www.charlespetzold.com/dotnet/\" target=\"_blank\"
title=\"New Window\">^</a>]"
"My Settings"="Select \"My Settings\" in the drop down below your name
at the top right"
These values are extracted from the Registry into our vector by means of the RegEnumValue() function (see DataReader.cpp) as follows:
for (dwIndex = 0; lStatus == ERROR_SUCCESS; ++dwIndex)
{
cchValueName = _countof(szKeyText);
cbData = 0;
lStatus = RegEnumValue(hkSnippets, dwIndex, szKeyText, &cchValueName, NULL, NULL, NULL, &cbData); if (lStatus == ERROR_SUCCESS)
{
pData = new BYTE[cbData];
#if (_WIN32_WINNT >= 0x0600) // if Windows Vista or later
lStatus = RegGetValue(hkSnippets, NULL, szKeyText,
RRF_RT_REG_SZ, NULL, pData, &cbData);
#else
lStatus = RegQueryValueEx(hkSnippets, szKeyText, NULL, NULL, pData, &cbData);
#endif
}
if (lStatus == ERROR_SUCCESS)
{
if (pvPairs == NULL)
{
pvPairs = new VECPAIR();
}
PTSTR pszContent = reinterpret_cast<PTSTR>(pData);
STRPAIR itemPair(szKeyText, pszContent);
pvPairs->push_back(itemPair);
delete[] pData;
}
}
The function extracts the name of each value entry within the key and, optionally, its content via a simple loop as shown above. As each entry is extracted, the data is used to create a new pair object which is then pushed into the vector that is used to hold all the items. The RegEnumValue() function returns a status of ERROR_NO_MORE_ITEMS when all values have been enumerated.
An alternative, and possibly better method, is to read the data from an XML file. This is not as difficult as it might be with the availability of the XMLLite library from Microsoft: see this article, and the Programmer's Guide.
The structure of the XML data may be in any form that the developer wishes, and the extraction code is then written to handle the element and attribute nodes in a forward direction reading through the XML as a stream. In order to implement the snippets that I commonly use, I have CDATA nodes when the value items contain special characters, including < and >, which would otherwise not be allowed. Thus, the XML data I have created contains items in the following form, corresponding to the items previously shown in the section on Registry values:
="1.0"
<snippets xmlns:dt="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:datatypes">
<snippet title="Use pre tags">
<