Introduction
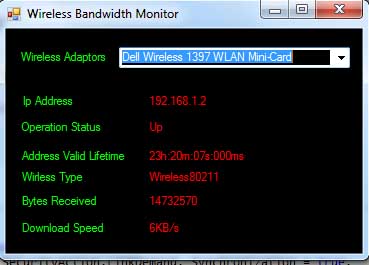
This article explains creating a simple tool which will display the current bandwidth and other
meta information about a selected wireless network card
attached to your machine. If multiple wireless cards are attached to the machine then the tool has the ability to detect all of them. And
the user can select which
card we are interested in monitoring. Moreover this tool can be expanded to work with Ethernet adapters as well.
Background
.NET allows you to access all the network interface card information via the NetworkInterface.GetAllNetworkInterfaces() method.
By applying LINQ filtering we can filter the information to capture only wireless interface information. Afterwards it’s just manipulating the inbuilt properties.
The code in this tool will help you calculate the number of bytes sent
by the wireless device. And to measure the current download speed of your selected wireless adaptor along with it you
will be able to gain access to the IP address associated with the
wireless interface using
the
UnicastIPAddressInformation class.
Using the Code
The first thing that we have do is detect all the wireless devises available in your machine and populate them into the dropdownbox:
using System.Net.NetworkInformation;
IEnumerable<NetworkInterface> nics = NetworkInterface.GetAllNetworkInterfaces().Where(
network => network.NetworkInterfaceType == NetworkInterfaceType.Wireless80211);
cmbAdptors.DisplayMember = "Description";
cmbAdptors.ValueMember= "Id";
foreach (NetworkInterface item in nics)
{
cmbAdptors.Items.Add(item);
}
if (cmbAdptors.Items.Count > 0)
cmbAdptors.SelectedIndex = 0;
Once the user changes the devises or initially when the first device is selected the
selected index change event will fire and we can capture the IP address and then call
the BandwidthCalculator method. In addition we need to start the timer which will update information every second:
private void cmbAdptors_SelectedIndexChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
try
{
if (cmbAdptors.SelectedItem is NetworkInterface)
{
slectedNic = cmbAdptors.SelectedItem as NetworkInterface;
uniCastIPInfo = null;
if (slectedNic != null && slectedNic.GetIPProperties().UnicastAddresses != null)
{
UnicastIPAddressInformationCollection ipInfo = slectedNic.GetIPProperties().UnicastAddresses;
foreach (UnicastIPAddressInformation item in ipInfo)
{
if (item.Address.AddressFamily == System.Net.Sockets.AddressFamily.InterNetwork)
{
lblIP.Text = item.Address.ToString();
uniCastIPInfo = item;
break;
}
}
}
BandwidthCalculator(uniCastIPInfo, slectedNic);
wirelssUpdator.Enabled = true;
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw;
}
}
The BandwidthCalculator method which will perform the updates:
public void BandwidthCalculator(UnicastIPAddressInformation ipInfo , NetworkInterface selecNic)
{
try
{
if (selecNic == null)
return;
lblType.Text = selecNic.NetworkInterfaceType.ToString();
lblOp.Text = selecNic.OperationalStatus.ToString();
IPv4InterfaceStatistics interfaceData = selecNic.GetIPv4Statistics();
int bytesRecivedSpeedValue = (int)(interfaceData.BytesReceived - double.Parse(lblReceived.Text)) / 1024;
lblReceived.Text = interfaceData.BytesReceived.ToString();
lblSpeed.Text = bytesRecivedSpeedValue.ToString() + "KB/s";
if (ipInfo != null)
{
TimeSpan addressLifeTime = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(ipInfo.AddressValidLifetime);
lblVallifetime.Text = string.Format("{0:D2}h:{1:D2}m:{2:D2}s:{3:D3}ms",
addressLifeTime.Hours,
addressLifeTime.Minutes,
addressLifeTime.Seconds,
addressLifeTime.Milliseconds);
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
}
}
Updating the timer:
private void wirelssUpdator_Tick(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
BandwidthCalculator(uniCastIPInfo, slectedNic);
}
Points of Interest
You can extend this application to work with the below interface types
- Wireless80211
- Ethernet
- MobileBroadbandGSM
- MobileBroadbandCDMA
- etc..
Points to Remember
Make sure that you are using .NET 3.5 or higher. Also you will need at least one wireless interface attached to your system.
